Short-Term Effects of Visceral Manual Therapy on Autonomic Nervous System Modulation in Individuals with Clinically Based Bruxism: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40710170
- PMCID: PMC12293791
- DOI: 10.3390/dj13070325
Short-Term Effects of Visceral Manual Therapy on Autonomic Nervous System Modulation in Individuals with Clinically Based Bruxism: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
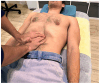
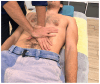
Background/Objectives: Bruxism has been associated with dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Visceral manual therapy (VMT) has shown beneficial effects on the vagal tone and modulation of ANS activity. This study aimed to evaluate the immediate and short-term effects of VMT in individuals with clinically based bruxism. Methods: A single-blind randomized controlled trial was conducted including 24 individuals with clinically based bruxism. Participants received two sessions of either VMT or a sham placebo technique. Outcome measures included heart rate variability (HRV), both normal-to-normal intervals (HRV-SDNN), and the root mean square of successive normal-to-normal intervals (HRV-RMSSD), as well as muscle tone and stiffness and pressure pain thresholds (PPTs). Measurements were made at T1 (baseline), T2 (post-first intervention), T3 (pre-second intervention), T4 (post-second intervention), and T5 (4-week follow-up). Results: A significant time*group interaction was observed for HRV-SDNN (p = 0.04, η2 = 0.12). No significant changes were found for muscle tone or stiffness. PPTs significantly increased at C4 after the second session (p = 0.049, η2 = 0.16) and at the left temporalis muscle after the first session (p = 0.01, η2 = 0.07). Conclusions: The findings suggest that two sessions of VMT may lead to significant improvements in HRV-SDNN compared to the placebo, suggesting a modulatory effect on autonomic function. No consistent changes were observed for the viscoelastic properties of the masticatory muscles. Isolated improvements in pressure pain sensitivity were found at C4 and the left temporalis muscle. Further research with larger sample sizes and long-term follow-up is needed to determine the clinical relevance of VMT in the management of signs and symptoms in individuals with bruxism.
Keywords: autonomic nervous system; bruxism; diaphragm; musculoskeletal manipulations; physical therapy modalities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wieckiewicz M., Bogunia-Kubik K., Mazur G., Danel D., Smardz J., Wojakowska A., Poreba R., Dratwa M., Chaszczewska-Markowska M., Winocur E., et al. Genetic Basis of Sleep Bruxism and Sleep Apnea-Response to a Medical Puzzle. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:7497. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64615-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous