Targeting DNA Damage Response-Mediated Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanistic Insights to Drug Development
- PMID: 40710178
- PMCID: PMC12293334
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol32070367
Targeting DNA Damage Response-Mediated Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanistic Insights to Drug Development
Abstract
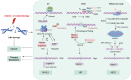
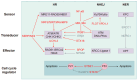
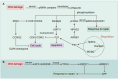
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains a major contributor to cancer-related deaths worldwide, with therapeutic resistance presenting a critical clinical hurdle. The DNA damage response (DDR) constitutes a sophisticated cellular framework that detects, signals, and repairs genetic lesions to preserve genomic stability. While the DDR plays a crucial role in determining the efficacy of radiotherapy and chemotherapy, current research primarily focuses on direct DDR inhibitors, often overlooking the broader regulatory networks that modulate DDR activity. This review aims to comprehensively analyze the upstream and downstream pathways governing DDR in NSCLC, highlighting key molecular regulators, signaling interactions, and potential feedback mechanisms contributing to therapy resistance. By identifying novel regulatory targets and clinically relevant biomarkers, we propose innovative therapeutic strategies to enhance treatment efficacy. Our approach seeks to bridge the gap between DDR dysregulation and precision oncology, offering new perspectives on overcoming resistance and improving patient outcomes in NSCLC.
Keywords: DNA damage response; chemotherapy; drug resistance; homologous recombination; non-homologous end joining; non-small cell lung cancer; radiotherapy; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

