Standardized Workflow and Analytical Validation of Cell-Free DNA Extraction for Liquid Biopsy Using a Magnetic Bead-Based Cartridge System
- PMID: 40710315
- PMCID: PMC12293894
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14141062
Standardized Workflow and Analytical Validation of Cell-Free DNA Extraction for Liquid Biopsy Using a Magnetic Bead-Based Cartridge System
Abstract
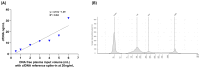
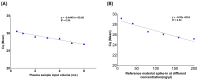
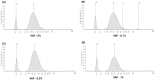
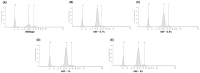
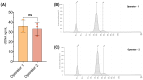
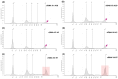
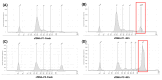
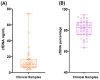
Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is an important biomarker for various cancer types, enabling a non-invasive testing approach. However, pre-analytical variables, including sample collection, tube type, processing conditions, and extraction methods, can significantly impact the yield, integrity, and overall quality of cfDNA. This study presents a comprehensive analytical validation of a magnetic bead-based, high-throughput cfDNA extraction system, with a focus on assessing its efficiency, reproducibility, and compatibility with downstream molecular applications. The validation was performed using a range of sample types: synthetic cfDNA spiked into DNA-free plasma, multi-analyte ctDNA plasma controls, Seraseq ctDNA reference material in a plasma-like matrix, extraction specificity controls, residual clinical specimen from patients, and samples from healthy individuals stored at room temperature or 4 °C for up to 48 h to assess stability. Extracted cfDNA was analyzed for concentration, percentage, and fragment size, using the Agilent TapeStation. Variant detection was evaluated using a next-generation sequencing (NGS) assay on the Seraseq ctDNA reference material. The results demonstrated high cfDNA recovery rates, consistent fragment size distribution (predominantly mononucleosomal and dinucleosomal), minimal genomic DNA (gDNA) contamination, and strong concordance between detected and expected variants in reference materials. The workflow also showed robust performance under different study parameters, variable sample conditions, including sample stability and integrity. Together, these findings confirm the efficiency and reliability of the evaluated cfDNA extraction system and underscore the importance of standardized pre-analytical workflows for the successful implementation of liquid biopsy for early cancer detection, therapeutic monitoring, and improved patient outcomes.
Keywords: TapeStation; cancer detection; cell-free DNA; cfDNA extraction; liquid biopsy; reference materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Impact of Higher Cell-Free DNA Yields on Liquid Biopsy Testing in Glioblastoma Patients.Clin Chem. 2025 Jan 3;71(1):215-225. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvae178. Clin Chem. 2025. PMID: 39749509
-
Evaluation of variability in cell-free DNA extraction efficiency from plasma and urine and spike-in normalization.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22999. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06563-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596083 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Free DNA in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Oncologist. 2017 Sep;22(9):1049-1055. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0178. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28778958 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Utility of ctDNA Analysis in Lung Cancer-A Review.Adv Respir Med. 2025 Jun 12;93(3):17. doi: 10.3390/arm93030017. Adv Respir Med. 2025. PMID: 40558116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

