Mechanistic Insights into Autophagy-Dependent Cell Death (ADCD): A Novel Avenue for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 40710325
- PMCID: PMC12293531
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14141072
Mechanistic Insights into Autophagy-Dependent Cell Death (ADCD): A Novel Avenue for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
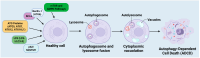
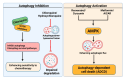
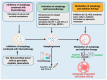
Autophagy-dependent cell death (ADCD) presents a promising but challenging therapeutic strategy in cancer treatment. Autophagy regulates cellular breakdown and stress responses, serving a dual function-either inhibiting tumorigenesis or facilitating the survival of cancer cells in advanced stages. This paradox presents both opportunities and challenges in the exploration of autophagy as a potential target for cancer treatment. In this review, we explore various pharmacological agents, including autophagy inhibitors (e.g., chloroquine, 3-MA) and activators (e.g., rapamycin, metformin), which have demonstrated effectiveness in modulating autophagy-dependent cell death (ADCD). These agents either enhance cancer cell apoptosis or sensitize tumors to conventional therapies. Combination therapies, such as the use of autophagy modulators alongside chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiation therapy, offer enhanced therapeutic potential by overcoming drug resistance and improving overall treatment efficacy. Nonetheless, significant challenges remain, including tumor heterogeneity, treatment resistance, and off-target effects of autophagy-targeting agents. Future progress in biomarker discovery, precision medicine, and targeted medication development will be crucial for enhancing ADCD-based methods. Although autophagy-dependent cell death presents significant potential in cancer treatment, additional studies and clinical validation are necessary to confirm its position as a conventional therapeutic approach. Therefore, this review aims to identify the existing restrictions that will facilitate the development of more effective and personalized cancer therapies, hence enhancing patient survival and outcomes.
Keywords: autophagy; autophagy-dependent cell death; cancer therapy; molecular mechanisms; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Metabolic stress-mediated cell death and autophagy in human lung cancer cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2025 Jun;392(6):103598. doi: 10.1016/j.jpet.2025.103598. Epub 2025 May 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2025. PMID: 40479744
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Mar;10(9):1-132. iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10090. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16545208
-
Oncolytic reovirus enhances the effect of CEA immunotherapy when combined with PD1-PDL1 inhibitor in a colorectal cancer model.Immunotherapy. 2025 Apr;17(6):425-435. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2501926. Epub 2025 May 12. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40353308
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

