Regulatory Functions of microRNAs in Cancer Stem Cells: Mechanism, Facts, and Perspectives
- PMID: 40710326
- PMCID: PMC12293480
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14141073
Regulatory Functions of microRNAs in Cancer Stem Cells: Mechanism, Facts, and Perspectives
Abstract
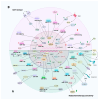
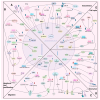
Cancer represents a significant global health hazard marked by elevated morbidity and mortality rates. Furthermore, the majority of tumor therapies encounter challenges, including metastasis, recurrence, and drug resistance. Consequently, it is essential to identify a specific and efficient tumor treatment approach. In recent years, the ongoing investigation and comprehension of tumors have led to significant attention towards cancer stem cells (CSCs). CSCs can facilitate tumor progression via self-renewal, differentiation capabilities, and multidrug resistance. Their function as a fundamental contributor to tumor heterogeneity, drug resistance, recurrence, and metastasis has emerged as a significant focus in cancer therapy research. In recent years, microRNAs (miRNAs) have been identified as crucial post-transcriptional regulators in biological processes, including chemosensitivity, self-renewal, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis of cancer stem cells (CSCs). This paper systematically reviews the molecular mechanisms through which miRNAs influence the characteristics of cancer stem cells by targeting essential genes (e.g., SOX2, EGFR, c-Met) and modulating signaling pathways, including Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, Hedgehog, and PI3K/Akt. Furthermore, we investigated the viability of miRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis evaluation, examined the similarities and attributes of pivotal miRNAs in modulating cancer stem cell functionality, and deliberated on therapeutic approaches stemming from miRNA regulation of cancer stem cell activity. We anticipate that this research will yield novel insights into targeted cancer therapy.
Keywords: biomarkers; cancer stem cells; chemotherapy resistance; miRNAs; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest directly related to this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An update on cancer stem cell survival pathways involved in chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer.Future Oncol. 2025 Mar;21(6):715-735. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2461443. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39936282 Review.
-
Molecular Biomarkers and Signaling Pathways of Cancer Stem Cells in Colorectal Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241254061. doi: 10.1177/15330338241254061. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38794896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A MicroRNA Screen Identifies the Wnt Signaling Pathway as a Regulator of the Interferon Response during Flavivirus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02388-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28148804 Free PMC article.
-
DSG3 promotes bladder cancer growth and metastasis via AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 2;23(1):729. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06754-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40605005 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Clarke M.F., Dick J.E., Dirks P.B., Eaves C.J., Jamieson C.H., Jones D.L., Visvader J., Weissman I.L., Wahl G.M. Cancer stem cells—Perspectives on current status and future directions: AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9339–9344. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3126. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

