Natural Killer (NK) Cell Alloreactivity in Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation
- PMID: 40710344
- PMCID: PMC12293795
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14141091
Natural Killer (NK) Cell Alloreactivity in Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
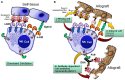
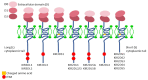
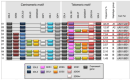
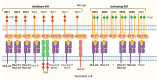
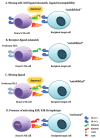
This paper conducts a literature review on the role of natural killer cells in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Theoretical concepts related to KIR genes are introduced regarding their structure, nomenclature, genetic organization, polymorphism, and inheritance pattern, types of KIR proteins and receptors, HLA ligands for KIR receptors, and the definition of different NK alloreactivity prediction models for the donor of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and the recipient. These models include the following and consider incompatibility: ligand-ligand, receptor-ligand, gene-gene, and KIR haplotype models or the KIR-B donor group. These models consider the presence or absence of specific ligands or receptors and/or KIR genes in the donor and recipient to predict alloreactivity. Determining the best model for predicting KIR alloreactivity and its significance in donor selection algorithms for haploidentical transplantation is still under investigation.
Keywords: alloreactivity; haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; natural killer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cooley S., Weisdorf D.J., Guethlein L.A., Klein J.P., Wang T., Le C.T., Marsh S.G.E., Geraghty D., Spellman S., Haagenson M.D., et al. Donor selection for natural killer cell receptor genes leads to superior survival after unrelated transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2010;116:2411–2419. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-283051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

