The Role of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) and Circulating Endothelial Cells (CECs) as Early Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Children with Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 40710348
- PMCID: PMC12293122
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14141095
The Role of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) and Circulating Endothelial Cells (CECs) as Early Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Children with Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
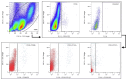
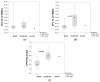
The aim of this study is to assess endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and circulating endothelial cells (CECs) at the time of type 1 diabetes (T1D) recognition concerning patients' clinical state, remaining insulin secretion, and further partial remission (PR) occurrence. We recruited 45 children that were admitted to hospital due to newly diagnosed T1D (median age 10.8 yrs), and 20 healthy peers as a control group. EPC and CEC levels were measured at disease onset in PBMC isolated from whole peripheral blood with the use of flow cytometry. Clinical data regarding patients' condition, C-peptide secretion, and further PR prevalence were analyzed. T1D-diagnosed patients presented higher EPC levels than the control group (p = 0.026), while no statistical differences in CEC levels and EPC/CEC ratio were observed. Considering only T1D patients, those with better clinical conditions presented lower EPCs (p = 0.021) and lower EPC/CEC ratios (p = 0.0002). Patients with C-peptide secretion within a normal range at disease onset presented lower EPC/CEC ratios (p = 0.027). Higher levels of EPCs were observed more frequently in patients with higher glucose, decreased fasting C-peptide, and lower stimulated C-peptide (all p < 0.05). The presence of DKA was related to higher EPC/CEC ratios (p = 0.034). Significantly higher levels of CECs were observed in patients who presented partial remission of the disease at 6 months after diagnosis (p = 0.03) only. In the study group, positive correlations of CECs with age, BMI at onset, and BMI in following years were observed. EPC/CEC ratios correlated positively with glucose levels at hospital admission and negatively with age, BMI, pH, and stimulated C-peptide level. We reveal a new potential for the application of EPCs and CECs as biomarkers, reflecting both endothelial injury and reconstruction processes in children with T1D. There is a need for further research in order to reduce cardiovascular risk in children with T1D.
Keywords: children; endothelial function; type 1 diabetes; vascular complications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Intensive glucose control versus conventional glucose control for type 1 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 14;2014(2):CD009122. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009122.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24526393 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Circulating Endothelial Cells as Direct Marker of Endothelial Damage in Allo-Transplant Recipients at High Risk of Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease/Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome.Transplant Cell Ther. 2024 Jun;30(6):580.e1-580.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2024.03.026. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Transplant Cell Ther. 2024. PMID: 38582286
-
Residual beta-cell function in children with type 1 diabetes after a partial remission phase - a possible relation between C-peptide and betatrophin.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 18;16:1602777. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1602777. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40607224 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of periodontal disease for glycaemic control in people with diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 6;2015(11):CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 14;4:CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub4. PMID: 26545069 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Lespagnol E., Dauchet L., Pawlak-Chaouch M., Balestra C., Berthoin S., Feelisch M., Roustit M., Boissière J., Fontaine P., Heyman E. Early Endothelial Dysfunction in Type 1 Diabetes Is Accompanied by an Impairment of Vascular Smooth Muscle Function: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020;11:203. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00203. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

