Pleural Empyema in Spain (2016-2022): A Nationwide Study on Trends in Hospitalizations, Mortality, and Impact of Comorbidities
- PMID: 40710380
- PMCID: PMC12296154
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm15070263
Pleural Empyema in Spain (2016-2022): A Nationwide Study on Trends in Hospitalizations, Mortality, and Impact of Comorbidities
Abstract
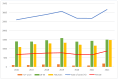
Background: Pleural empyema (PE) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. This study aimed to analyze the epidemiological characteristics of patients hospitalized for PE in Spain between 2016 and 2022. Methods: This retrospective observational study of PE cases was based on the hospital discharge records from the National Health System between 2016 and 2022. The variables analyzed were sex, age, comorbidities, discharge diagnoses and procedures, overall severity, whether empyema was a primary or secondary diagnosis, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), length of stay (LOS), in-hospital mortality, and healthcare costs. Results: Between 2016 and 2022, 19864 PE cases were diagnosed in Spain, revealing an overall rate of 0.64 per 1000 hospitalizations, with the exception of a slight decline in 2021. The mean age of the patients with PE was 61 years, and 73.85% were men. Most patients had low comorbidities, with a median Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) of 1.7. Most cases (63%) involved secondary diagnoses (pneumonia, pneumococcal pneumonia, sepsis, COVID, or lung cancer). The in-hospital mortality rate was higher in the secondary diagnosis group than in the primary diagnosis group (13.4% vs. 6.2%, respectively, p < 0.001). The factors associated with increased mortality included older age (≥66 years), higher CCI scores, ICU admission, and shorter LOS (<10 days). Conversely, pleural drainage and pneumonia as secondary diagnoses were protective factors. Conclusions: PE is an increasingly common pathology in clinical practice, especially in older and frail patients. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality, and its prognosis worsens with age and comorbidities. Therefore, early and appropriate diagnosis and standardized management strategies are required to mitigate the mortality and healthcare costs.
Keywords: Spain; comorbidity pneumonia; mortality; pleural drainage; pleural empyema; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Surgical versus non-surgical management for pleural empyema.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 17;3(3):CD010651. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010651.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28304084 Free PMC article.
-
Sex as a prognostic factor for mortality in adults with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 20;3(3):CD013835. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013835.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40110896
-
Automated monitoring compared to standard care for the early detection of sepsis in critically ill patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 25;6(6):CD012404. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012404.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29938790 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical versus non-surgical management of pleural empyema.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD001956. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001956. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Oct 19;(4):CD001956. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001956.pub2. PMID: 12076430 Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources