Investigating Systemic Metabolic Effects of Betula alba Leaf Extract in Rats via Urinary Metabolomics
- PMID: 40710571
- PMCID: PMC12300340
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo15070471
Investigating Systemic Metabolic Effects of Betula alba Leaf Extract in Rats via Urinary Metabolomics
Abstract
Background/objectives: Herbal extracts from Betula alba (birch) are traditionally used for their purported diuretic effects, but scientific evidence supporting these claims remains limited. In this pilot study, we evaluated the short-term effects of a standardized B. alba leaf extract in healthy adult rats using an untargeted urinary metabolomics approach based on UPLC-QTOF.
Methods: Two doses, 25 or 50 mg/kg, of a standardized B. alba extract were orally administered to rats. The extract contains hyperoside (0.53%), quercetin glucuronide (0.36%), myricetin glucoside (0.32%), and chlorogenic acid (0.28%) as its main constituents. After 3 days of treatment, the 24 h urine output was measured.
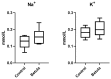
Results: While no statistically significant changes were observed in the 24 h urine volume or the urinary Na+ and K+ excretion, multivariate metabolomic analysis revealed treatment-induced alterations in the urinary metabolic profile. Notably, the levels of two glucocorticoids, i.e., corticosterone and 11-dehydrocorticosterone, were increased in treated animals, suggesting that the extract may influence corticosteroid metabolism or excretion, potentially impacting antidiuretic hormone signaling. Elevated bile-related compounds, including bile acids and bilin, and glucuronidated metabolites were also observed, indicating changes in bile acid metabolism, hepatic detoxification, and possibly gut microbiota activity.
Conclusions: Although this study did not confirm a diuretic effect of B. alba extract, the observed metabolic shifts suggest broader systemic bioactivities that warrant further investigation. Overall, the results indicate that the approach based on urinary metabolomics may be valuable in uncovering the mechanisms of action and evaluating the bioactivity of herbal extracts with purported diuretic properties.
Keywords: Betula alba; metabolomics; natural diuretics; polyphenols; urine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oral herbal therapies for treating osteoarthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 22;2014(5):CD002947. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002947.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24848732 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Popowski D., Kruk A., Pawłowska K.A., Dolzkho D., Korczak M., Piwowarski J.P., Roszko M., Granica S. Evaluating Birch Leaf Tea as a Functional Herbal Beverage: Beneficial Impact on the Urinary Tract, and Metabolism in Human Organism. Food Res. Int. 2024;189:114481. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114481. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

