The Robust Vessel Segmentation and Centerline Extraction: One-Stage Deep Learning Approach
- PMID: 40710596
- PMCID: PMC12295992
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging11070209
The Robust Vessel Segmentation and Centerline Extraction: One-Stage Deep Learning Approach
Abstract
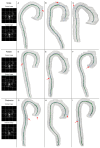
The accurate segmentation of blood vessels and centerline extraction are critical in vascular imaging applications, ranging from preoperative planning to hemodynamic modeling. This study introduces a novel one-stage method for simultaneous vessel segmentation and centerline extraction using a multitask neural network. We designed a hybrid architecture that integrates convolutional and graph layers, along with a task-specific loss function, to effectively capture the topological relationships between segmentation and centerline extraction, leveraging their complementary features. The proposed end-to-end framework directly predicts the centerline as a polyline with real-valued coordinates, thereby eliminating the need for post-processing steps commonly required by previous methods that infer centerlines either implicitly or without ensuring point connectivity. We evaluated our approach on a combined dataset of 142 computed tomography angiography images of the thoracic and abdominal regions from LIDC-IDRI and AMOS datasets. The results demonstrate that our method achieves superior centerline extraction performance (Surface Dice with threshold of 3 mm: 97.65%±2.07%) compared to state-of-the-art techniques, and attains the highest subvoxel resolution (Surface Dice with threshold of 1 mm: 72.52%±8.96%). In addition, we conducted a robustness analysis to evaluate the model stability under small rigid and deformable transformations of the input data, and benchmarked its robustness against the widely used VMTK toolkit.
Keywords: computed tomography angiography images; multitask neural network; one-stage centerline reconstruction; vascular modeling toolkit; vessel centerline extraction; vessel segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Luo Z., Cai J., Peters T.M., Gu L. Intra-operative 2-D ultrasound and dynamic 3-D aortic model registration for magnetic navigation of transcatheter aortic valve implantation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2013;32:2152–2165. - PubMed
-
- Shimura S., Odagiri S., Furuya H., Okada K., Ozawa K., Nagase H., Yamaguchi M., Cho Y. Echocardiography-guided aortic cannulation by the Seldinger technique for type A dissection with cerebral malperfusion. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020;159:784–793. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2019.02.097. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

