Interpretable Prediction and Analysis of PVA Hydrogel Mechanical Behavior Using Machine Learning
- PMID: 40710711
- PMCID: PMC12294283
- DOI: 10.3390/gels11070550
Interpretable Prediction and Analysis of PVA Hydrogel Mechanical Behavior Using Machine Learning
Abstract
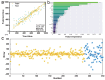
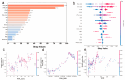
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogels have emerged as versatile materials due to their exceptional biocompatibility and tunable mechanical properties, showing great promise for flexible sensors, smart wound dressings, and tissue engineering applications. However, rational design remains challenging due to complex structure-property relationships involving multiple formulation parameters. This study presents an interpretable machine learning framework for predicting PVA hydrogel tensile strain properties with emphasis on mechanistic understanding, based on a comprehensive dataset of 350 data points collected from a systematic literature review. XGBoost demonstrated superior performance after Optuna-based optimization, achieving R2 values of 0.964 for training and 0.801 for testing. SHAP analysis provided unprecedented mechanistic insights, revealing that PVA molecular weight dominates mechanical performance (SHAP importance: 84.94) through chain entanglement and crystallization mechanisms, followed by degree of hydrolysis (72.46) and cross-linking parameters. The interpretability analysis identified optimal parameter ranges and critical feature interactions, elucidating complex non-linear relationships and reinforcement mechanisms. By addressing the "black box" limitation of machine learning, this approach enables rational design strategies and mechanistic understanding for next-generation multifunctional hydrogels.
Keywords: PVA hydrogel; SHAP analysis; feature importance; hyperparameter optimization; interpretable machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Data-driven framework for prediction of mechanical properties of waste glass aggregates concrete.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20902. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05229-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594120 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilizing machine learning for reproducible and explainable results: A novel validation approach to subject-specific insights.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025 Sep;269:108899. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2025.108899. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40570739
-
Application of machine learning for predicting the incubation period of water droplet erosion in metals.Discov Appl Sci. 2025;7(7):712. doi: 10.1007/s42452-025-07268-8. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Discov Appl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40612685 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches for predicting dairy cattle methane emissions: from traditional methods to machine learning.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae219. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae219. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39123286 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Li Z., Yin F., He W., Hang T., Li Z., Zheng J., Li X., Jiang S., Chen Y. Anti-Freezing, Recoverable and Transparent Conductive Hydrogels Co-Reinforced by Ethylene Glycol as Flexible Sensors for Human Motion Monitoring. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023;230:123117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.123117. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Zhang L., Lu A. Highly Stretchable, Transparent Cellulose/PVA Composite Hydrogel for Multiple Sensing and Triboelectric Nanogenerators. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020;8:13935–13941. doi: 10.1039/D0TA02010A. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

