Advances in Genetic Risk Scores for Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40710902
- PMCID: PMC12298128
- DOI: 10.3390/neurolint17070099
Advances in Genetic Risk Scores for Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Research concerning the genetic risk for dementia has recently been headed towards new directions. Novel findings from genome-wide association studies have highlighted the association of Alzheimer's disease incidence with many gene polymorphisms, apart from the Apolipoprotein-E genotype. The identification of additional genetic risk factors has led to the construction of specific genetic risk scores for dementia, considering many different genetic factors and specific biological pathways related to Alzheimer's disease.
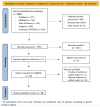
Methods: We conducted a systematic review following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis method, summarizing existing data regarding genetic risk scores for Alzheimer's disease and dementia, in order to improve the current understanding of the genetic underpinnings of dementia. In specific, five databases (PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, Web of science, and Cochrane Central) were searched using the keywords "genetic risk score", "Alzheimer's disease", and "dementia" with specific inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results: From the 552 articles identified, we finally included 20 studies for the qualitative analysis. These reports were classified in three different categories of genetic scores: "polygenic risk scores (PRSs)" (including 11 studies), "pathway specific polygenic risk scores (p-PRSs)" (5 studies), and "complex genetic risk scores" (4 studies).
Conclusions: Existing genetic risk scores have contributed to better dementia prediction and a better understanding of the underlying pathology. Novel approaches integrating multiple polygenic risk scores might ameliorate the accuracy of genetic risk scores. The combination of polygenic risk scores that are specific to related biological pathways or relevant biomarkers is of utmost importance to achieve a better predictive ability.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biological pathways; dementia; genetic risk scores; polygenic risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
18F PET with florbetapir for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 22;11(11):CD012216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012216.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29164603 Free PMC article.
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
-
18F PET with flutemetamol for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 22;11(11):CD012884. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012884. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29164602 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 10;2014(6):CD008782. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008782.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24913723 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources