Exploratory Evaluation for Functional Changes of Six-Month Systematic Non-Invasive Electrical Stimulation in a Whole-Body Suit on Children with Cerebral Palsy GMFCS III-V
- PMID: 40710905
- PMCID: PMC12298194
- DOI: 10.3390/neurolint17070102
Exploratory Evaluation for Functional Changes of Six-Month Systematic Non-Invasive Electrical Stimulation in a Whole-Body Suit on Children with Cerebral Palsy GMFCS III-V
Abstract
Background/objectives: Spasticity in children with cerebral palsy (CP) can impair motor-related functions. The objective of this exploratory, prospective study was to examine if transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) in a whole-body suit leads to changes in spasticity and other related effects.
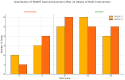
Methods: Thirty-one children with CP GMFCS III-V, with a median age of 11.0 years (age range of 7-17 years), were consecutively included, and they used the suit with TENS for 24 weeks. The primary outcome was spasticity measured using the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS). Functional motor-related tasks were evaluated by the Goal Attainment Scale (SMART GAS). The Modified Tardieu Scale (MTS), passive Range of Motion (pROM), GMFM-66, and Posture and Postural Ability Scale (PPAS) assessments were performed.
Results: Seventeen subjects (17/31) completed the 24 weeks. Dropout was due to difficulty in donning the suit. The level of overall spasticity, most pronounced in the proximal arms and legs, was reduced according to the MAS, but not the MTS or pROM. Subject-relevant motor-related goals improved significantly in standing/walking and hand/arm function. Changes in the GMFM-66 and PPAS were not significant.
Conclusions: Although there were statistically significant but underpowered changes in the MAS after 24 weeks, there were no clinically relevant effects. Exploratorily, we found observer-reliant motor-related functional improvements, which, however, we were unable to detect when trying to quantify them. Donning the suit led to dropout throughout the study. Caregivers need to allocate time, mental capacity and have the physical skill set for donning the suit for long-term use.
Keywords: cerebral palsy; child; electrical stimulation; goals; movement disorder; muscle spasticity; neurorehabilitation; posture; prospective study; range of motion.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest for all authors. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 9;10(10):CD012172. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012172.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28990665 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal baclofen for treating spasticity in children with cerebral palsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 13;2015(11):CD004552. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004552.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26563961 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of lower limb spasticity in cerebral palsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD001408. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001408. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. PMID: 10796784
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for neuropathic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 14;9(9):CD011976. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011976.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28905362 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 8;1:CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub8. PMID: 36384212 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Eunson P. Aetiology and epidemiology of cerebral palsy. [(accessed on 28 April 2025)];Paediatr. Child. Health. 2016 26:367–372. doi: 10.1016/j.paed.2016.04.011. Available online: https://www.physio-pedia.com/images/4/47/Aetiology_and_Epidemiology_of_C.... - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

