Anti-IFN-γ Autoantibody Syndrome Presenting with Disseminated Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections: A Case Series of Therapeutic Implications and Review of Literature
- PMID: 40711078
- PMCID: PMC12301023
- DOI: 10.3390/tropicalmed10070202
Anti-IFN-γ Autoantibody Syndrome Presenting with Disseminated Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections: A Case Series of Therapeutic Implications and Review of Literature
Abstract
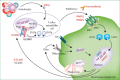
Anticytokine autoantibodies (AAbs), particularly anti-interferon-gamma (anti-IFN-γ) AAbs, disrupt cytokine functions, leading to infections, autoimmune-like diseases, and conditions resembling interleukin-12 (IL-12)/IFN-γ pathway defects. Advances in genetic testing have clarified overlaps between autoinflammatory, autoimmune disorders, and primary immunodeficiencies but reveal complex phenotypes and pathways. While these insights deepen our understanding of immune mechanisms, they also complicate diagnosis and treatment, with limited options for IFN-γ deficiencies caused by genetic mutations. The adult-onset immunodeficiency with disseminated lymphadenitis due to nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) and other opportunistic infections has been linked to high levels of anti-IFN-γ AAbs. This syndrome, initially identified in HIV-negative Asian patients, frequently affects individuals of Asian descent and may be associated with specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles. The presence of neutralizing anti-IFN-γ AAbs impairs the IFN-γ-dependent immune response, likely contributing to the persistent NTM infection. This study underscores the potential for late-onset anti-IFN-γ AAb syndrome to manifest with disseminated NTM (dNTM) infections, highlights the importance of timely diagnosis and considers rituximab as a potential therapeutic option.
Keywords: case series; immune deficiency; interferon gamma; mycobacterium avium complex; nontuberculous mycobacteria; rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Aoki A., Sakagami T., Yoshizawa K., Shima K., Toyama M., Tanabe Y., Moro H., Aoki N., Watanabe S., Koya T., et al. Clinical Significance of Interferon-γ Neutralizing Autoantibodies Against Disseminated Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018;66:1239–1245. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix996. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

