Nanofabrication Techniques for Enhancing Plant-Microbe Interactions in Sustainable Agriculture
- PMID: 40711205
- PMCID: PMC12299764
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15141086
Nanofabrication Techniques for Enhancing Plant-Microbe Interactions in Sustainable Agriculture
Abstract
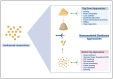
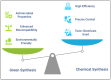
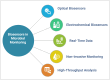
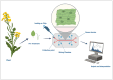
Nanomaterials have emerged as a transformative technology in agricultural science, offering innovative solutions to improve plant-microbe interactions and crop productivity. The unique properties, such as high surface area, tunability, and reactivity, of nanomaterials, including nanoparticles, carbon-based materials, and electrospun fibers, render them ideal for applications such as nutrient delivery systems, microbial inoculants, and environmental monitoring. This review explores various types of nanomaterials employed in agriculture, focusing on their role in enhancing microbial colonization and soil health and optimizing plant growth. Key nanofabrication techniques, including top-down and bottom-up manufacturing, electrospinning, and nanoparticle synthesis, are discussed in relation to controlled release systems and microbial inoculants. Additionally, the influence of surface properties such as charge, porosity, and hydrophobicity on microbial adhesion and colonization is examined. Moreover, the potential of nanocoatings and electrospun fibers to enhance seed protection and promote beneficial microbial interactions is investigated. Furthermore, the integration of nanosensors for detecting pH, reactive oxygen species, and metabolites offers real-time insights into the biochemical dynamics of plant-microbe systems, applicable to precision farming. Finally, the environmental and safety considerations regarding the use of nanomaterials, including biodegradability, nanotoxicity, and regulatory concerns, are addressed. This review emphasizes the potential of nanomaterials to revolutionize sustainable agricultural practices by improving crop health, nutrient efficiency, and environmental resilience.
Keywords: electrospinning; microbial inoculants; nanocoatings; nanomaterials; nanosensors; plant-microbe interactions; surface properties; sustainable agriculture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Carbon quantum dots as versatile nanomaterials for improving soil health and plant stress tolerance: a comprehensive review.Planta. 2025 Jul 9;262(2):44. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04758-2. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40632315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Agro-Nanotechnology in African Agriculture: A Path to Sustainable Development-Systematic Review.ScientificWorldJournal. 2025 Mar 17;2025:9073364. doi: 10.1155/tswj/9073364. eCollection 2025. ScientificWorldJournal. 2025. PMID: 40129615 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles on the Soil-Plant System and Their Potential Agricultural Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Jun 19;15(12):950. doi: 10.3390/nano15120950. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40559314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ruminant nutrition symposium: novel microbial solutions to optimize production efficiency in beef and dairy systems.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf165. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf165. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40372016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biopriming with Endophytes improves plant resilience to develop climate-smart, futuristic agricultural crops.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 28;41(8):272. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04485-6. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40719792 Review.
References
-
- Choudhary D.K., Varma A., Tuteja N. Plant-Microbe Interaction: An Approach to Sustainable Agriculture. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2017.
-
- Mohanram S., Kumar P. Rhizosphere microbiome: Revisiting the synergy of plant-microbe interactions. Ann. Microbiol. 2019;69:307–320. doi: 10.1007/s13213-019-01448-9. - DOI
-
- Mabrouk Y., Hemissi I., Salem I.B., Mejri S., Saidi M., Belhadj O. Potential of rhizobia in improving nitrogen fixation and yields of legumes. Symbiosis. 2018:107. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.73495. - DOI
-
- Tahat M.M., Alananbeh K.M., Othman Y.A., Leskovar D.I. Soil health and sustainable agriculture. Sustainability. 2020;12:4859. doi: 10.3390/su12124859. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

