Utility of Urinary miRNA Biomarkers for Canine Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnostics
- PMID: 40711281
- PMCID: PMC12298497
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci12070621
Utility of Urinary miRNA Biomarkers for Canine Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnostics
Abstract
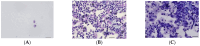
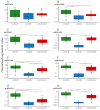
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is one of the most frequent tumors in dogs. Besides cytology, histology, and testing for a BRAF mutation, non-invasive biomarkers would benefit the early detection and therapy of UC. This study aimed to compare the detectability of miRNAs in urine sediment and supernatant and to assess their potential as biomarkers for UC. The study involved two phases with 47 canine samples in total; in a pilot trial, ten different miRNAs (miR-16, 21, 103b, 106b, 146, 155, 182, 221, 222, and 375) were isolated from the urine sediments and supernatants from seven healthy control dogs and seven dogs with UC. In a further step, eight miRNAs were isolated from urine sediments from 18 healthy dogs, 11 dogs with purulent cystitis, and 18 dogs with UC. The detectability of miRNAs was improved when isolated from the urine sediment compared with the supernatant. MiR-16 was not deregulated, and miR-106b showed significantly lower expression in cystitis compared with the control. Lower copy numbers were seen for miR-21, 182, 221, and 222 in cystitis cases compared with the controls and UC, respectively. Deregulation was observed for miR-155 and miR-375 between all three groups. A panel including miR-182, 221, 222, 155, and 375 has the potential to discriminate among all three groups in a two-step approach.
Keywords: biomarker; cystitis; dog; miRNA; urine; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors A.K., H.A.-L., M.B., A.-L.v.d.W., and M.A. were employed by the company LABOKLIN GmbH&Co.KG. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Urinary microRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers for Predicting the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Aug 13;17(16):2640. doi: 10.3390/cancers17162640. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867269 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

