CNS Involvement by North American-Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma Is Associated With Discrete Dissemination Patterns and Molecular Profiles, Involving XPO1 E571 and KLF2/PI3KCD in Selected Cases
- PMID: 40712110
- PMCID: PMC12309975
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.23.00526
CNS Involvement by North American-Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma Is Associated With Discrete Dissemination Patterns and Molecular Profiles, Involving XPO1 E571 and KLF2/PI3KCD in Selected Cases
Abstract
Purpose: CNS involvement in North American adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (NA-ATLL) remains poorly understood. This study examined the CNS involvement in patients with ATLL treated at a tertiary hospital in New York City.
Methods: CNS involvement was defined by positive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytology, flow cytometry, positive CNS imaging, or neurological examination findings.
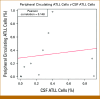
Results: Among 94 patients with NA-ATLL, 21 (22.3%) had CNS involvement. CSF was involved in 13 patients at diagnosis and five at relapse. Magnetic resonance imaging detected brain and spinal involvement in 24% and 14% of the patients, respectively. Results of neurological examinations were abnormal in 33% and 14% of the patients at diagnosis and relapse, respectively. The XPO1 E571K mutation was found in two patients with extensive, treatment-refractory CNS disease, with a median overall survival (OS) of 2 months. Other mutations, including KLF2 and PI3KCD, were noted in two patients. The median OS was 8.5 months, and the median relapse-free survival (RFS) was 6.5 months in our series. In most cases (5/21), the lymphomatous phenotype appeared to have a direct mass-like extension, whereas in patients with predominant blood involvement tended to spread to the CSF by traversing the blood-brain barrier.
Conclusion: In this report, we describe the patterns of CNS involvement in ATLL and their association with mutations. We also describe two rapidly fatal cases with the XPO1 E571K mutation, which may represent a novel therapeutic target for T-cell lymphomas.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for people with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 13;9(9):CD013365. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013365.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34515338 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Uncommon Non-MS Demyelinating Disorders of the Central Nervous System.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s11910-025-01432-8. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40591029 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources