Synthesis of 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) coated platinum nanoparticles and apoptotic effects on U87 human glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 40713567
- PMCID: PMC12291401
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03893-w
Synthesis of 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) coated platinum nanoparticles and apoptotic effects on U87 human glioblastoma cells
Abstract
Background: 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is a widely used chemotherapeutic agent; however, its clinical application is often limited by systemic toxicity and the development of drug resistance. To enhance its therapeutic efficacy, novel drug delivery strategies are under investigation. This study evaluated the use of platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) as a nanocarrier system for 5-FU delivery to glioblastoma cells, focusing on their effects on apoptosis-related proteins.
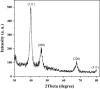
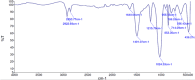
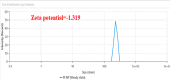
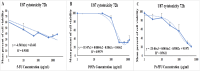
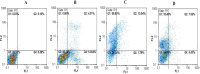
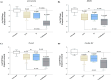
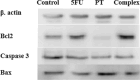
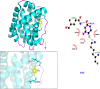
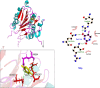
Methods: The binding affinity and interactions of 5-FU with key apoptotic proteins (BAX, Bcl2, and Caspase-3) were assessed using molecular docking and validated through molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. PtNPs were synthesized and characterized via scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Drug loading and encapsulation efficiency were determined, and cytotoxicity assays were conducted in U87 glioblastoma cells. The expression levels of apoptosis-related genes and proteins were evaluated to determine the biological impact of the formulations.
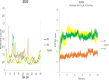
Results: Docking results confirmed effective binding of 5-FU to Bcl2, Caspase-3, and BAX, with MD simulations supporting stable complex formation, particularly with Bcl2 and Caspase-3. The synthesized PtNPs exhibited favorable physicochemical properties, including uniform morphology and high drug loading efficiency. In vitro release studies revealed a sustained release profile for the PtNPs/5-FU formulation. Furthermore, PtNPs/5-FU significantly downregulated the expression of EMT- and proliferation-related genes (cyclin D1, ZEB1, and Twist) and suppressed Bcl2 protein levels, resulting in enhanced apoptosis in U87 cells.
Conclusion: PtNPs effectively functioned as a delivery platform for 5-FU, improving its release kinetics and promoting apoptotic responses while potentially minimizing systemic toxicity. These findings support further exploration of PtNP-based drug delivery systems as a promising strategy for glioblastoma treatment.
Keywords: 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU); Apoptosis; Drug delivery; Glioblastoma; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics simulation; Platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of Fe3O4 biosynthesized through the green synthesis of Silybum marianum and HA in the targeted delivery of 5-Fluorouracil to HCT116 cell line.Daru. 2025 Jul 31;33(2):27. doi: 10.1007/s40199-025-00568-9. Daru. 2025. PMID: 40742481
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Development and evaluation of a Cu(II) complex as nanosuspension for enhanced antitumor efficacy against glioblastoma cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27304. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13081-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715522 Free PMC article.
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(15):iii-ix, xi-162. doi: 10.3310/hta12150. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462574
-
Elucidating the Mechanism of Xiaoqinglong Decoction in Chronic Urticaria Treatment: An Integrated Approach of Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics Analysis, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.2174/0115734099391401250701045509. Online ahead of print. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 40676786
References
-
- Stupp R, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

