The role of maternal infections in neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders: focus on the P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β signalling pathway
- PMID: 40713568
- PMCID: PMC12298051
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03509-0
The role of maternal infections in neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders: focus on the P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β signalling pathway
Abstract
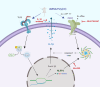
Immune activation in the prenatal and early postnatal periods is increasingly implicated in the aetiology of neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia, by disrupting critical neurodevelopmental processes. The impact of immune activation on brain development can be influenced by the type, timing, location, and severity of the infection. Viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections, as well as maternal autoimmune diseases, can lead to the activation of the purinergic P2X7 receptors, thereby contributing to neuroinflammation. Upon activation, P2X7 induces the assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β. Besides activation of additional inflammatory mediators, excessive IL-1β during critical periods of brain development can disrupt neuronal migration, synapse formation, dendritic morphology and blood-brain barrier integrity, contributing to a range of neurodevelopmental abnormalities. Animal studies have shown that inhibiting the components of the P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β pathway can mitigate these adverse effects. This review examines the role of the P2X7/NLRP3/IL-1β pathway in mediating the effects of infection and neuronal inflammation on brain development. We discuss the therapeutic potential of targeting this pathway with a balanced approach that reduces long-term neuronal inflammation while preserving essential immune functions.
Keywords: Interleukin-1β; Maternal immune activation; NLRP3; Neurodevelopment; Neurodevelopmental disorders; P2X7; Prenatal infection.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complement Molecule C3a Exacerbates Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Inducing Neuroinflammation Through the C3aR-ERK-P2X7-NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Axis.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):1791-1810. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02155-7. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39528767
-
Hypothermia protects against ventilator-induced lung injury by limiting IL-1β release and NETs formation.Elife. 2025 Jun 24;14:RP101990. doi: 10.7554/eLife.101990. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40553503 Free PMC article.
-
FCV activates NLRP3 inflammasome through ion-dependent pathway to promote IL-1β secretion.Vet Microbiol. 2025 Aug;307:110628. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2025.110628. Epub 2025 Jun 28. Vet Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40602240
-
New Insights on the Potential Role of Pyroptosis in Parkinson's Neuropathology and Therapeutic Targeting of NLRP3 Inflammasome with Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based miRNA Therapeutics.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul;62(7):9365-9384. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04818-4. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40100493 Review.
-
Decoding NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Alzheimer's Disease: A Focus on Receptor Dynamics.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10792-10812. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04918-1. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40232645 Review.
References
-
- Spaans F, et al. Danger signals from ATP and adenosine in pregnancy and preeclampsia. Hypertension. 2014;63(6):1154–60. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues RJ, Marques JM, Cunha RA. Purinergic signalling and brain development. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;95:34–41. - PubMed
-
- Pelegrin P. P2X7 receptor and the NLRP3 inflammasome: Partners in crime. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;187:114385. - PubMed
-
- Di Virgilio F, et al. The P2X7 Receptor in Infection and Inflammation. Immunity. 2017;47(1):15–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

