The role of endolysosomal progranulin and TMEM106B in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 40713630
- PMCID: PMC12297828
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-025-00873-6
The role of endolysosomal progranulin and TMEM106B in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
Although different neurodegenerative diseases are defined by distinct pathological proteins, they share many common features including protein aggregation. Despite this commonality, most current therapeutic approaches in the field, such as anti-aggregate antibodies, are focused on individual diseases or single neuropathologies with only limited success. The endolysosomal proteins progranulin and TMEM106B were both initially associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration but have subsequently also been linked to other neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, these proteins are predicted to participate in common pathogenic pathways shared across various neurodegenerative diseases. Importantly, recent discoveries of TMEM106B amyloid fibrils in varied neurodegenerative diseases and glycosphingolipid regulation by progranulin and TMEM106B further support their central roles in cross-disease neurodegenerative mechanisms. This review summarizes recent advances in progranulin and TMEM106B function within the endolysosomal system and neurodegenerative diseases. It describes preclinical models and therapeutic approaches for progranulin- and TMEM106B-associated diseases. We also discuss future direction leading to novel alternative therapies targeting shared mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Aging; Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid fibrils; Endolysosome; Frontotemporal Lobar degeneration; GBA1; Glycosphingolipid; Parkinson’s disease; Progranulin; TMEM106B.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
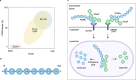
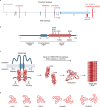
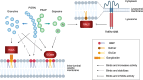
References
-
- Wilson DM 3rd, Cookson MR, Van Den Bosch L, Zetterberg H, Holtzman DM, Dewachter I. Hallmarks of neurodegenerative diseases. Cell. 2023;186(4):693–714. - PubMed
-
- Kovacs GG. Are comorbidities compatible with a molecular pathological classification of neurodegenerative diseases? Curr Opin Neurol. 2019;32(2):279–91. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Telpoukhovskaia MA, Bahr BA, Chen X, Gan L. Endo-lysosomal dysfunction: a converging mechanism in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018;48:52–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

