Histone H4 lysine 20 methylation marks genes dynamically regulated during erythroid maturation
- PMID: 40713835
- PMCID: PMC12296644
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-025-00609-2
Histone H4 lysine 20 methylation marks genes dynamically regulated during erythroid maturation
Abstract
Background: Methylation of H4K20 has been implicated in the regulation of gene expression but also plays essential roles in numerous cellular functions, making studies of its effects on transcription challenging. To gain insights into the role of H4K20 methylation in regulating gene expression, we studied H4K20me1 and H4K20me3 in the context of the well-characterized erythroid differentiation of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
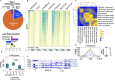
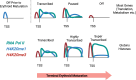
Results: H4K20me1 enrichment over the gene body was strongly correlated with expression changes. During erythroid differentiation, there was a dramatic decline in the level of RNA Polymerase II (Pol II); H4K20me1 was lost where Pol II was lost, and gained at genes where Pol II occupancy was maintained and transcripts were upregulated. We did identify a small subset of highly expressed genes, including beta-globin, that had a dramatic loss of H4K20me1 during erythroid differentiation, despite a substantial gain of Pol II. The histone demethylase PHF8 was present at these genes, as well as at the transcription start site of many active genes. In contrast to H4K20me1 over gene bodies correlating with transcription, enrichment at the transcription start site occurred at genes with low levels of Pol II occupancy and RNA expression throughout erythroid differentiation. The majority of H4K20me3 was present over intergenic regions, consistent with its well-established role as a repressor of repetitive elements. Intriguingly, H4K20me3 was also present at the transcription start site of genes with H4K20me1 over the gene body. At these genes, H4K20me3 levels were highly correlated with chromatin accessibility at the transcription start site, and an elevated Pol II pausing index. There was a dramatic loss of H4K20me3 occupancy in genic, but not intergenic, regions during erythroid differentiation.
Conclusions: There are dynamic changes in H4K20 methylation during cellular differentiation that correlate strongly with Pol II occupancy and activity. These changes occurred in genic regions, with H4K20me3 at the transcription start site correlated with Pol II pausing, and H4K20me1 gene body levels tightly linked with transcriptional changes. Together, these data provide important insights into the role of H4K20 methylation in the regulation of gene expression during cellular differentiation.
Keywords: Differentiation; Erythropoiesis; H4K20me1; H4K20me3; Histone methylation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A dual role for the histone methyltransferase PR-SET7/SETD8 and histone H4 lysine 20 monomethylation in the local regulation of RNA polymerase II pausing.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 14;289(11):7425-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.520783. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24459145 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of U2AF1 mutation on erythroid differentiation and sensitivity to demethylation drug treatment.Med Oncol. 2025 Aug 31;42(10):459. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02956-2. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40886238
-
The SAMD1 transcription factor coordinates hematopoietic lineage differentiation and H3K4 methylation status.Blood Adv. 2025 Aug 12;9(15):3988-4003. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024015627. Blood Adv. 2025. PMID: 40402130 Free PMC article.
-
Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4(4):CD009016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27098439 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

