PhyloTune: An efficient method to accelerate phylogenetic updates using a pretrained DNA language model
- PMID: 40715068
- PMCID: PMC12297363
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61684-3
PhyloTune: An efficient method to accelerate phylogenetic updates using a pretrained DNA language model
Abstract
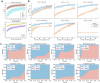
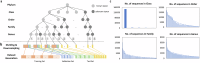
Understanding the phylogenetic relationships among species is crucial for comprehending major evolutionary transitions. Despite the ever-growing volume of sequence data, constructing reliable phylogenetic trees effectively becomes more challenging for current analytical methods. In this study, we introduce a new solution to accelerate the integration of novel taxa into an existing phylogenetic tree using a pretrained DNA language model. Our approach identifies the taxonomic unit of a newly collected sequence using existing taxonomic classification systems and updates the corresponding subtree. Specifically, we leverage a pretrained BERT network to obtain high-dimensional sequence representations, which are used not only to determine the subtree to be updated, but also identify potentially valuable regions for subtree construction. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, named PhyloTune, through experiments on simulated datasets, as well as our curated Plant (focusing on Embryophyta) and microbial (focusing on Bordetella genus) datasets. Our findings provide evidence that phylogenetic trees can be constructed by automatically selecting the most informative regions of sequences, without manual selection of molecular markers. This discovery offers a guide for further research into the functional aspects of different regions of DNA sequences, enriching our understanding of biology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Ciccarelli, F. D. et al. Toward automatic reconstruction of a highly resolved tree of life. Science311, 1283–1287 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Hug, L. A. et al. A new view of the tree of life. Nat. Microbiol.1, 1–6 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Winter, M., Devictor, V. & Schweiger, O. Phylogenetic diversity and nature conservation: where are we? Trends Ecol. Evol.28, 199–204 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

