Tumour initiated purinergic signalling promotes cardiomyocyte RBFOX1 degradation and cardiotoxicity from DNA damaging anticancer agents
- PMID: 40715150
- PMCID: PMC12297588
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62172-4
Tumour initiated purinergic signalling promotes cardiomyocyte RBFOX1 degradation and cardiotoxicity from DNA damaging anticancer agents
Abstract
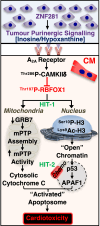
It is well established tumour cells secrete signalling factors affecting distant normal tissues. What remains unresolved is whether these factors initiate a signalling cascade rendering terminally differentiated cardiomyocytes susceptible to apoptosis, a feature of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity (CIC). Here we show in MANTICORE trial cancer patients, cumulative baseline plasma levels of the nucleoside inosine and its derivative hypoxanthine predict cardiotoxicity. We found the Zn2+ finger transcription factor ZNF281 increases synthesis and release of inosine and hypoxanthine, which bind the A2A receptor on cardiomyocytes, activating CAMKIIδ which phosphorylates the postnatal mRNA splicing factor RBFOX1, resulting in its caspase-dependent degradation. RBFOX1 loss reverts cardiomyocytes to a less mature state with open chromatin and susceptibility to DNA damage, apoptosis or CIC, when treated with DNA intercalating or alkylating anticancer agents. These findings suggest cumulative inosine and hypoxanthine levels may be a biomarker predicting patient susceptibility to DNA damaging anti-cancer agents.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FNDC5/irisin mitigates the cardiotoxic impacts of cancer chemotherapeutics by modulating ROS-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Redox Biol. 2025 Mar;80:103527. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103527. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 39923397 Free PMC article.
-
The function of PCSK9 in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and its underlying mechanism.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03419-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593844 Free PMC article.
-
CDC20 protects the heart from doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by modulating CCDC69 degradation.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Mar 5;30(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00708-8. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40045239 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
-
Dexrazoxane for preventing or reducing cardiotoxicity in adults and children with cancer receiving anthracyclines.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 27;9(9):CD014638. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014638.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36162822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tisdale, M. J. Cachexia in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer2, 862–871 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Lenihan, D. J. & Cardinale, D. M. Late cardiac effects of cancer treatment. J. Clin. Oncol.30, 3657–3664 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Moslehi, J. J. Cardiovascular toxic effects of targeted cancer therapies. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 1457–1467 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

