Chromosome-level genome assembly of Sinocyclocheilus jii based on PacBio HiFi and Hi-C sequencing
- PMID: 40715168
- PMCID: PMC12297406
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05663-9
Chromosome-level genome assembly of Sinocyclocheilus jii based on PacBio HiFi and Hi-C sequencing
Abstract
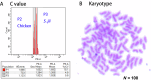
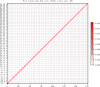
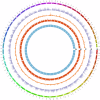
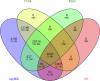
Sinocyclocheilus jii, a cavefish species endemic to China, belongs to the genus Sinocyclocheilus within the family Cyprinidae. Species within this genus exhibit significant morphological differentiation, making it not only the most species-rich genus within Cyprinidae in China but also the most diverse group of cavefishes worldwide. However, the limited availability of genomic resources has limited investigations into the genetic basis of trait variations, phylogenetic relationships, and adaptive evolution in this genus. In this study, we assembled a chromosome-level reference genome for S. jii by integrating PacBio HiFi long reads, Illumina short reads, and Hi-C sequencing data. Flow cytometry was used to estimate the genome size prior to assembly, providing a key step in technical validation. The final genome assembly spans 1.75 Gb with a contig N50 of 35.0 Mb. Using Hi-C sequencing data, the assembled scaffolds were successfully anchored to 50 chromosomes. The completeness of the chromosome-level assembly was estimated at 98.9% by BUSCO analysis. Genome annotation identified 855.5 Mb of repetitive sequences and predicted a total of 52,867 protein-coding genes, of which 51,932 genes were functionally annotated. This study presents a high-quality chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of S. jii, providing a fundamental genomic resource for future phylogenetic and evolutionary studies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of Spinibarbus caldwelli.Sci Data. 2025 Jul 3;12(1):1138. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05469-9. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40610506 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-scale assembly of the Xenocypris davidi using PacBio HiFi reads and Hi-C technologies.Sci Data. 2025 Mar 18;12(1):452. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04800-8. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40102422 Free PMC article.
-
Assembling chromosome-level genomes of male and female Chanodichthys mongolicus using PacBio HiFi reads and Hi-C technologies.Sci Data. 2025 Jun 6;12(1):949. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05120-7. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40481035 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Wang, D. & Chen, Y. The Origin and Adaptive Evolution of The Genus. Sinocyclocheilus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin.24, 630–634 (2000).
-
- Liu, T. Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships among 30 Species of the Genus Sinocyclocheilus Based on RAD-Seq Technology (in Chinese). MSc thesis, Yunnan University (2020).
-
- Zhang, C. & Dai, D. A new species of Sinocyclocheilus from China—Sinocyclocheilus jii (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae: Barbinae). Acta Zootaxon Sin.17, 377–380 (1992).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

