Salidroside ameliorates diabetic amyotrophy by targeting Caspase-3 to inhibit apoptosis
- PMID: 40715275
- PMCID: PMC12297698
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12704-1
Salidroside ameliorates diabetic amyotrophy by targeting Caspase-3 to inhibit apoptosis
Abstract
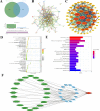
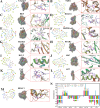
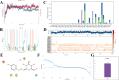
In this study, the Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes model in rats was employed to assess and verify the activity of salidroside (SAL) in ameliorating diabetic amyotrophy (DA). Network pharmacology analysis was used to obtain SDS-related targets, DA-related targets, and their intersectional targets. After subjecting the targets to GO enrichment and KEGG pathway analysis, a network "target pathway for SAL in ameliorating DA" was set up. Next, the Schrodinger Maestro 13.5 software was utilized for molecular docking to ascertain the binding free energy and binding mode between SAL and target proteins. Molecular dynamics simulations were performed using the Desmond program. Saturation mutation analysis was performed using Schrodinger's Maestro 13.5 software. SPR technology was used to explore the affinity between SAL and Caspase-3 protein. The expression level of Cleaved-Caspase-8, Caspase-8 p18, Cleaved-Caspase-3, Caspase-3 p17, PARP, and PARP P85 proteins in gastrocnemius tissue were determined by Western blotting (WB) analysis. In an STZ-induced rat diabetic model, SAL treatment significantly (P < 0.05) reduced blood glucose levels and increased forepaw force. HE and Masson staining results indicated that SAL treatment could significantly increase the mean muscle fiber area (P < 0.01) and decrease fibrosis (P < 0.05). Immunohistochemical results revealed that SAL treatment significantly increased (P < 0.01) the expression of Myogenin and decreased (P < 0.001) the expression of FBXO32 in gastrocnemius muscle tissue. Network pharmacological analysis identified that there were a total of 61 intersection proteins, among which TNF, APP, Caspase-3, PPARG, NQO1, HDAC1, BCL2, SRC, HDAC6, ACE, MAPK3, HSP90AA1, ATM, and REN emerged as potential core targets for SAL to ameliorate DA. Based on the crystal structure of the potential core protein, the complex structure model of the core target-SAL was created using molecular docking (XP mode of flexible docking), and the MMGBS analysis was carried out. The SPR results data demonstrated specific binding and kinetic compatibility between the SAL and Caspase-3 proteins. The results of WB revealed that compared with the model group, SAL significantly decreased (P < 0.05) expression of Cleaved Caspase-3, Caspase-3 p17, and PARP P85, and significantly increased (P < 0.05) the expression of PARP1, while the expression of Cleaved Caspase-8 and Caspase-8 p18 remained unchanged. These results suggest that Caspase-3 is a potential target for SAL to ameliorate DA which eventually plays a role in ameliorating DA by regulating apoptosis-related pathways, which provides a theoretical basis along with clues for the research and development of SAL as ameliorating DA drugs.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase-3; Computational biology; Diabetic amyotrophy; Network pharmacology; Salidroside.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergies of dibutyl phthalate on high-fat diet can aggravate cardiac fibrosis/dysfunction and the protective effects of vitamin E and salidroside: A molecular toxicological study in Sprague-Dawley rats.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025 Sep 1;302:118708. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.118708. Epub 2025 Jul 19. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025. PMID: 40684633
-
Elucidating the Mechanism of Xiaoqinglong Decoction in Chronic Urticaria Treatment: An Integrated Approach of Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics Analysis, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.2174/0115734099391401250701045509. Online ahead of print. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 40676786
-
Assessing the potential impact of salidroside on Chikungunya virus-induced acute interstitial nephritis via network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro experiments.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 22;15:1623860. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1623860. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40766840 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and over.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(19):iii-iv, 1-360. doi: 10.3310/hta12190. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18485271
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Feng, L. et al. Prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in patients with diabetes: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.107, 1470–1483 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BS202307/PhD research startup foundation of Changzhi Medical College
- BS202306/PhD research startup foundation of Changzhi Medical College
- 2024L281/Shanxi University science and technology innovation plan project
- 2024L280/Shanxi University science and technology innovation plan project
- 202403021222311/Supported by Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

