Comparison of rebamipide and tegoprazan combination therapy and tegoprazan monotherapy for ESD induced gastric ulcers a randomized multicenter study
- PMID: 40715454
- PMCID: PMC12297290
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11964-1
Comparison of rebamipide and tegoprazan combination therapy and tegoprazan monotherapy for ESD induced gastric ulcers a randomized multicenter study
Abstract
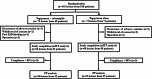
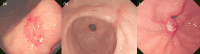
Currently, no consensus exists on optimal treatment for post-endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) gastric ulcer. This study aims to compare rebamipide and tegoprazan combination therapy with tegoprazan monotherapy for post-ESD ulcer healing. Between May 2022 and September 2023, 140 patients (141 lesions) who underwent ESD for gastric epithelial neoplasms at five tertiary hospitals were randomly assigned to tegoprazan monotherapy or combination therapy groups. The size, stage and healing quality of the post-ESD ulcers were assessed at weeks 4 and 8. Modified intention-to-treat (mITT) and per-protocol analyses included 132 and 121 lesions, respectively. The ulcer healing rate at week 4 was significantly higher in the combination therapy group than in the tegoprazan monotherapy group (96.4% vs. 93.6%, P = 0.02 in mITT). Combination therapy significantly predicted higher-than-average ulcer healing at week 4 (odds ratio 2.28, 95% confidence interval 1.04-5.02, P = 0.04). The proportion of flat ulcer scar at week 8 was significantly higher in the combination group than in the tegoprazan monotherapy group (73.8% vs. 48.4%, P = 0.007). Combination treatment with rebamipide and tegoprazan led to faster ulcer healing and the development of high-quality post-ESD scars compared to tegoprazan monotherapy.
Keywords: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Gastric ulcer; Rebamipide; Tegoprazan.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gotoda, T., Yamamoto, H. & Soetikno, R. M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol.41, 929–942. 10.1007/s00535-006-1954-3 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Liu, Q., Ding, L., Qiu, X. & Meng, F. Updated evaluation of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus surgery for early gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. (London, England)73, 28–41. 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.11.027 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Kim, Y. I. et al. Long-term survival after endoscopic resection versus surgery in early gastric cancers. Endoscopy47, 293–301. 10.1055/s-0034-1391284 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Pyo, J. H. et al. Long-term outcome of endoscopic resection vs. surgery for early gastric cancer: A non-inferiority-matched cohort study. Am. J. Gastroenterol.111, 240–249. 10.1038/ajg.2015.427 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Kosaka, T. et al. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: A single-center retrospective study. Dig. Endosc. Off. J. Jpn. Gastroenterol. Endosc. Soc.26, 183–191. 10.1111/den.12099 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

