Risk factors for prediabetes in young adults: a study based on Korea National health and nutrition examination survey data
- PMID: 40715513
- PMCID: PMC12297219
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13378-5
Risk factors for prediabetes in young adults: a study based on Korea National health and nutrition examination survey data
Abstract
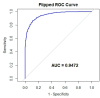
Diabetes is a growing health concern among young adults; yet, most studies focus on older populations. This study aimed to examine the factors associated with prediabetes development in young adults. We carried out a cross-sectional study using data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) for the period 2013-2021. Young adults were categorized into prediabetes (n = 2306) and normal glucose (n = 2306) groups. Propensity score matching was applied to control for age and sex, and multiple logistic regression was performed to identify significant predictors for prediabetes. The results showed that glycated hemoglobin had the highest adjusted Odds Ratio (OR = 2.27, p < 0.001), confirming its strong association with pre diabetes. Age group (OR = 2.27, p < 0.001), also showed a substantial effect, Sex (OR = 1.95, p < 0.001), physical activity (OR = 1.69, p < 0.001), Overweight (OR = 1.39, p < 0.0034) and Fasting blood sugar (OR = 1.33, p < 0.0034) were also significant predictors. However, alcohol consumption and underweight were not statistically significant. Metabolic indicators along with physical inactivity are critical factors influencing prediabetes in young adults. Early screening and targeted lifestyle interventions are essential in preventing diabetes progression, and reducing the risk of future health burdens.
Keywords: Early diagnosis; Prediabetes; Predictive modeling; Risk factors; Young adults.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical considerations: The study was conducted using publicly available, de-identified KNHANES data. Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Hallym University (Approval No.: HIRB-2024-056). All research procedures adhered to the ethical guidelines outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing knowledge, attitude, and dietary practice in association with prediabetes risk using objective clinical markers among Saudi adult population: A cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Apr 18;104(16):e42172. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042172. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40258756 Free PMC article.
-
The association of obesity and lipid-related indicators with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality risks in patients with diabetes or prediabetes: a cross-sectional study based on machine learning algorithms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 2;16:1492082. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1492082. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40529828 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-dimensional characterization of prediabetes in the Project Baseline Health Study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Jul 18;21(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01565-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35850765 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong, J. et al. Management of type 2 diabetes in young adults aged 18–30 years: ADS/ADEA/APEG consensus statement. Med. J. Aust. 216 (8), 422–429 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Lee, K. A. Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adolescents and young adults. J. Korean Diabetes. 21, 6–10 (2020).
-
- World Health Organization. Noncommunicable Diseases: Progress Monitor 2024 (WHO, 2024). https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240075016
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical