Predictive markers of obesity and glucose metabolism dysfunction in adult common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus)
- PMID: 40715578
- PMCID: PMC12532565
- DOI: 10.1038/s41366-025-01841-2
Predictive markers of obesity and glucose metabolism dysfunction in adult common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus)
Abstract
Objective: Characterize the effects of obesity on common marmoset glucose metabolism and develop predictive markers of glucose metabolism dysfunction.
Methods: Body size, weight, lean mass, fat mass, %fat, resting energy expenditure (REE), and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were measured on 51 adult marmosets. Physical activity was assessed using actimeter collars (n = 50). A body mass-per-length parameter (BML) was constructed. Animals were classified as without obesity or with obesity (%fat >10%) and by the age they obtained maximum weight (Maxwt). Correlation, MANOVA, and binary logistic regression were used to examine relationships between parameters; path analysis to explore directional relationships.
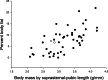
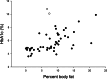
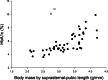
Results: Body fat and BML were correlated (r = 0.565, p < 0.001). Both were correlated with HbA1c (r = 0.658; r = 0.764, p < 0.001). Activity was negatively correlated with %fat and REE (r = -0.437, p = 0.002; r = -0.473, p < 0.001). REE was correlated with %fat, BML, and HbA1c (r > 0.5, p < 0.001). Marmosets with obesity were more likely to have elevated HbA1c (>5.7%; odds ratio = 8.25, p = 0.003). BML above 3.4 g/mm predicted obesity (OR = 6.25 [95% CI 1.62-24.02], p = 0.008) and high HbA1c (OR = 29.47 [95% CI 6.21-139.72], p < 0.001). Early Maxwt predicted increased fat mass (F = -0.476, p = 0.015) and high %fat (F = -0.084, p = 0.014).
Conclusion: Both %fat and BML were markers for high HbA1c. Early maximum adult weight predicts increased adiposity and risk of glucose dysfunction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

