Genetic variation in the activity of a TREM2-p53 signaling axis determines oxygen-induced lung injury
- PMID: 40715658
- PMCID: PMC12456008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02217-4
Genetic variation in the activity of a TREM2-p53 signaling axis determines oxygen-induced lung injury
Abstract
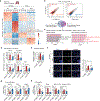
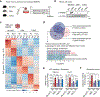
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is a common complication of preterm birth, driven in part by the inflammatory effects of supplemental oxygen on the immature lung. Although oxygen therapy is essential, it contributes to disrupted lung development but not all infants are equally susceptible. Using genetically diverse mouse models, we found that hyperoxia-sensitive mice exhibit a distinct innate immune response compared to resilient strains. Notably, the hyperoxia-sensitive C57BL/6J strain showed selective upregulation of TREM2 on lung macrophages and monocytes. Deletion of TREM2 in myeloid cells led to reduced inflammation, preserved alveolar structure and sustained cell proliferation in the developing lung following oxygen exposure. Mechanistically, TREM2 loss limited p53 activation, favoring cell-cycle arrest over apoptosis. These results identify TREM2 as a key driver of immune-mediated lung injury in neonatal hyperoxia and suggest it may be a promising therapeutic target for preventing or treating bronchopulmonary dysplasia in vulnerable preterm infants.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


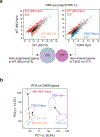


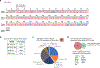
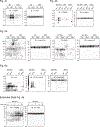
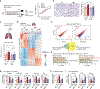



References
-
- Collaco JM, Eldredge LC & McGrath-Morrow SA Long-term pulmonary outcomes in BPD throughout the life-course. Journal of perinatology : official journal of the California Perinatal Association (2024). - PubMed
Methods-only references
-
- Ruifrok AC, Katz RL & Johnston DA Comparison of quantification of histochemical staining by hue-saturation-intensity (HSI) transformation and color-deconvolution. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 11, 85–91 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Ruifrok AC & Johnston DA Quantification of histochemical staining by color deconvolution. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 23, 291–299 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Wang L & Mao Q Probabilistic Dimensionality Reduction via Structure Learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41, 205–219 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

