Oxysterol-binding protein ORP6 regulates lipid metabolism and brain Aβ production
- PMID: 40716750
- PMCID: PMC12455110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100868
Oxysterol-binding protein ORP6 regulates lipid metabolism and brain Aβ production
Abstract
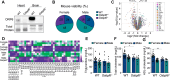
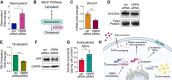
The mammalian brain is the most cholesterol-rich organ of the body, relying on in situ de novo cholesterol synthesis. Maintaining cholesterol homeostasis is crucial for normal brain function. Oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP)-related proteins (ORPs) are highly conserved cytosolic proteins that coordinate lipid homeostasis by regulating cell signaling, interorganelle membrane contact sites, and non-vesicular transport of cholesterol. Here, we show that ORP6 is highly enriched in the mammalian brain, particularly within neurons and astrocytes, with widespread expression across distinct brain regions, including the hippocampus, which is essential for learning and memory. Whole-body ablation of ORP6 (Osbpl6-/-) in mice resulted in dysregulation of systemic and brain lipid homeostasis, with elevated levels of brain desmosterol and amyloid-beta oligomers (AβOs). Mechanistically, ORP6 knockdown in astrocytes altered the expression of cholesterol metabolism genes, promoting the accumulation of esterified cholesterol in lipid droplets, reducing cholesterol efflux and plasma membrane cholesterol content, and increasing amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) processing. Our findings underscore the role of ORP6 in systemic and brain lipid homeostasis, highlighting its importance in maintaining overall brain health.
Keywords: amyloid beta; astrocyte; cholesterol efflux; high-density lipoprotein; lipid droplet; lipid metabolism; oxysterol-binding protein-like 6.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Maxfield F., Tabas I., Maxfield F.R., Tabas I. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 2006;438:612–621. - PubMed
-
- Vihervaara T., Jansen M., Uronen R.L., Ohsaki Y., Ikonen E., Olkkonen V.M. Cytoplasmic oxysterol-binding proteins: sterol sensors or transporters? Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2011;164:443–450. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

