Identification of a key smooth muscle cell subset driving ischemic cardiomyopathy progression through single-cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 40717095
- PMCID: PMC12301475
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-09928-6
Identification of a key smooth muscle cell subset driving ischemic cardiomyopathy progression through single-cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
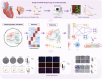
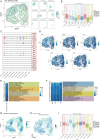
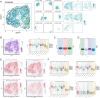
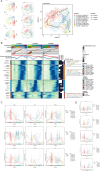
Cardiomyopathy encompasses a range of diseases that severely affect the complex functions of the heart, involving structural and functional abnormalities, and is associated with high mortality. Recent studies have highlighted the critical role of ferroptosis in regulating oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiomyopathy. In this study, we established that the C6 S100A4+ SMCs subpopulation is critical by performing an integrated single-cell analysis of the known publicly available data GSE145154. We validated the role of S100A4 in SMCs through in vitro experiments, providing evidence for its potential as a therapeutic target. Furthermore, these cells interact with endothelial cells through the PTN-NCL pathway, influencing disease progression. Key transcription factors, including KLF2, FOS, FOSB, and JUNB, were identified. This key subpopulation, along with its associated signaling pathways, marker genes, stemness genes, and transcription factors, may offer new insights for preventing the onset and progression of cardiomyopathy, particularly ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy; Exosomes; Ferroptosis; Inflammation; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Smooth muscle cells.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical statement: The study was reviewed and approved by Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Designation:AF/SC-08/03.0).
Figures





Similar articles
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the potential role of Postn(+) fibroblasts in promoting the progression of myocardial fibrosis after myocardial infarction.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22390. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04990-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595870 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Single-Cell and Spatial Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies ISR-Related Genes Driving Immune Regulation in Parkinson's Disease.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 15;18:9321-9341. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S521744. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40687147 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing technology was employed to construct a risk prediction model for genes associated with pyroptosis and ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma.Respir Res. 2025 Jul 18;26(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03323-5. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40682067 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Ferroptosis With Natural Products to Treat Diabetes and Its Complications: Opportunities and Challenges.Phytother Res. 2025 Jul 9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.70028. Online ahead of print. Phytother Res. 2025. PMID: 40634143 Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and its insights into cellular heterogeneity in atherosclerosis.Vascul Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;159:107499. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2025.107499. Epub 2025 May 7. Vascul Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40345606 Review.
References
-
- Maron, B. J. et al. Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: An American heart association scientific statement from the council on clinical cardiology, heart failure and transplantation committee; Quality of care and outcomes research and functional genomics and translational biology interdisciplinary working groups; And council on epidemiology and prevention. Circulation113, 1807–1816. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.174287 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Li, D., Pi, W., Sun, Z., Liu, X. & Jiang, J. Ferroptosis and its role in cardiomyopathy. Biomed. Pharmacother.153, 113279. 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113279 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Cardiomyopathies, B. E. An Overview. Circ. Res.121, 711–721. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311812 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Li, Y., Du, J., Liu, B. & She, Q. Identifying key genes and related molecules as potential biomarkers in human dilated cardiomyopathy by comprehensive bioinformatics analysis. Cardiovasc. Innov. Appl.8, 996. 10.15212/CVIA.2023.0018 (2023).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

