Plasma microRNA-210 is associated with VEGF-A and EphrinA3 and relates to coronary collateral circulation in patients with coronary heart disease: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40717103
- PMCID: PMC12302828
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-025-05013-y
Plasma microRNA-210 is associated with VEGF-A and EphrinA3 and relates to coronary collateral circulation in patients with coronary heart disease: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: This study explored the interrelationships among vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), microRNA-210 (miR-210), and EphrinA3 in the plasma of patients with coronary heart disease (CHD), and their collective influence on coronary collateral circulation (CCC) development.
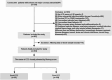
Methods: We enrolled 253 patients with ≥ 90% stenosis in at least one coronary artery, stratified into good CCC (n = 99) and poor CCC (n = 154) groups according to the Rentrop grading system. Plasma concentrations of miR-210, VEGF-A, and EphrinA3 were quantified via qRT-PCR and ELISA. The associations between these biomarkers and CCC status were evaluated through correlation analysis, multivariate regression, and mediation analysis.
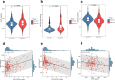
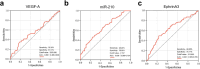
Results: Good CCC patients demonstrated significantly elevated plasma miR-210 (1.936 [1.099-4.118] vs. 1.272 [0.792-2.081], p < 0.001) and VEGF-A levels (3119.655 ± 850.995 vs. 2910.440 ± 713.218 pg/mL, p = 0.038), alongside reduced EphrinA3 levels (529.594 ± 143.037 vs. 584.657 ± 127.182 pg/mL, p = 0.002) compared to poor CCC patients. ROC analysis revealed AUCs of 0.656 (95% CI: 0.589-0.724) for miR-210, 0.563 (95% CI: 0.489-0.638) for VEGF-A, and 0.632 (95% CI: 0.560-0.705) for EphrinA3, which improved to 0.747, 0.696, and 0.744 respectively after adjustment for confounders. In fully adjusted multivariate models, miR-210 maintained a robust positive association with good CCC (OR: 1.558, 95% CI: 1.257-1.931, p < 0.001), with its highest tertile conferring 4.58-fold increased odds compared to the lowest tertile. Conversely, EphrinA3 exhibited a significant negative association (OR: 0.993, 95% CI: 0.990-0.997, p < 0.001), with its highest tertile linked to 79.4% reduced odds of good CCC. VEGF-A showed a modest association (OR: 1.001, p = 0.043). Notably, mediation analysis revealed that miR-210 functions as a pivotal intermediary in pathways connecting both VEGF-A and EphrinA3 to CCC formation, mediating 77.18% and 49.90% of their respective effects.
Conclusions: Plasma miR-210 levels exhibit a strong association with coronary collateral circulation development and represent a promising biomarker for CCC formation in patients with severe coronary stenosis. The influence of VEGF-A and EphrinA3 on CCC formation appears to be predominantly mediated through miR-210, highlighting its central role in coronary collateralization pathways.
Keywords: Collateral circulation; Coronary heart disease; EphrinA3; MicroRNA-210; VEGF-A.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All experimental procedures in this study were approved by the Ethics Review Committee at the Second Norman Bethune Hospital of Jilin University. We obtained written informed consents from all patients and carried out the study following the Helsinki declaration. Clinical trial number: not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The value of plasma immunoproteasome for predicting coronary collateral circulation in ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Biomark Med. 2025 Jul;19(13):509-516. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2025.2520158. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Biomark Med. 2025. PMID: 40536446
-
The relationship of plasma miR-503 and coronary collateral circulation in patients with coronary artery disease.Life Sci. 2018 Aug 15;207:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29870767
-
The Prognostic Potential of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 1 for Cardiovascular Complications in Peripheral Artery Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Jul 1;12(7):253. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12070253. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40710778 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor biosimilars for neovascular age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 3;6(6):CD015804. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015804.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38829176 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 10;2014(6):CD008782. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008782.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24913723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun XX, Li S, Fang W, Tian YQ, Shen R, Wei H, et al. Preserved myocardial viability in patients with chronic total occlusion of a single coronary artery. J Nucl Cardiol. 2021;28:2812–22. - PubMed
-
- Seiler C, Stoller M, Pitt B, Meier P. The human coronary collateral circulation: development and clinical importance. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2674–82. - PubMed
-
- Berry C, Balachandran KP, L’Allier PL, Lespérance J, Bonan R, Oldroyd KG. Importance of collateral circulation in coronary heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:278–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

