Establishment of Prediction Model of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis Before Operation for Early-Stage Breast Cancer
- PMID: 40717419
- PMCID: PMC12304652
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748251363328
Establishment of Prediction Model of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis Before Operation for Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Abstract
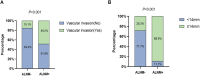
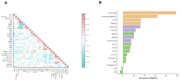
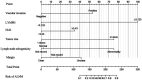
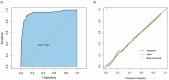
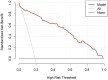
IntroductionThis study aimed to assess the predictive value of integrating ultrasonographic features, pathological characteristics, and inflammatory markers for axillary lymph node metastasis (ALNM) in early-stage breast cancer (BC), and to construct a corresponding nomogram.MethodsA retrospective review was conducted on clinical data from 287 early-stage BC patients who underwent surgery at Shenzhen Luohu People's Hospital between January 2020 and March 2024. Based on histopathological evaluation, patients were categorized into ALNM-positive (ALNM+) and ALNM-negative (ALNM-) groups. Independent predictors of ALNM were identified using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. These variables were used to develop a predictive nomogram. Model performance was evaluated by concordance index (C-index), receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration plot, and decision curve analysis (DCA), assessing its accuracy, discrimination, calibration, and clinical utility.ResultsMultivariate analysis identified vascular invasion, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte count, tumor size, lymph node echogenicity, and margin characteristics as independent predictors of ALNM. The nomogram showed excellent discriminative ability (AUC = 0.944, 95% CI: 0.906-0.981; C-index = 0.944, 95% CI: 0.906-0.982) and good calibration (Brier score = 0.063). DCA indicated meaningful clinical benefit across relevant threshold probabilities.ConclusionThe nomogram developed in this study demonstrates strong predictive performance and clinical value for preoperative ALNM assessment in early-stage BC. It may serve as a practical tool to guide individualized surgical and therapeutic decision-making.
Keywords: axillary lymph node metastasis (ALNM); breast cancer (BC); inflammatory markers; nomogram; risk.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Validated Ultrasound-Based Scoring System to Stratify Risk of Axillary Metastasis in Breast Cancer: AX-RADS (Axillary Imaging Reporting and Data System).J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jul;132(1):28-34. doi: 10.1002/jso.28159. Epub 2025 May 20. J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40392181
-
Developing and Evaluating a Nomogram Model Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Based on Multimodal Imaging Characteristics.Acad Radiol. 2025 Aug;32(8):4382-4394. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2025.04.031. Epub 2025 May 15. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40379590
-
Incorporating ultrasound-based lymph node staging significantly improves the performance of a clinical nomogram for predicting preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Jul 3;23(4):680-688. doi: 10.17305/bb.2022.8564. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36724018 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Jan;15(4):iii-iv, 1-134. doi: 10.3310/hta15040. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21276372 Free PMC article.
-
PET-CT for assessing mediastinal lymph node involvement in patients with suspected resectable non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 13;2014(11):CD009519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009519.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25393718 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

