Engineering of tissue in microphysiological systems demonstrated by modelling skeletal muscle
- PMID: 40717794
- PMCID: PMC12289553
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbaf059
Engineering of tissue in microphysiological systems demonstrated by modelling skeletal muscle
Abstract
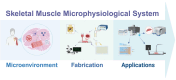
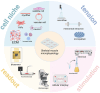
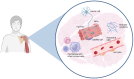
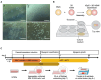
Research on myogenesis and myogenic pathologies has garnered significant attention in recent years. However, traditional in vitro modeling approaches have struggled to fully replicate the complex functions of skeletal muscle. This limitation is primarily due to the insufficient reconstruction of the muscle tissue microenvironment and the role of physical cues in regulating muscle cell activity. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of the microenvironment, which includes cells, extracellular matrix (ECM) and cytokines, in influencing myogenesis, regeneration and inflammation. This review focuses on advances in skeletal muscle construction toward a complete microphysiological system, such as organoids and muscle-on-a-chip technology, as well as innovative interventions like bioprinting and electrical stimulation. These advancements have enabled researchers to restore functional skeletal muscle tissue, bringing us closer to achieving a fully functional microphysiological system. Compared to traditional models, these systems allow for the collection of more comprehensive data, providing insights across multiple scales. Researchers can now study skeletal muscle and disease models in vitro with increased precision, enabling more advanced research into the physiological and biochemical cues affecting skeletal muscle activity. With these advancements, new applications are emerging, including drug screening, disease modeling and the development of artificial tissues. Progression in this field holds great promise for advancing our understanding of skeletal muscle function and its associated pathologies, offering potential therapeutic solutions for a variety of muscle-related diseases.
Keywords: bioengineering; in vitro modeling; microenvironment; microphysiological system; skeletal muscle.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
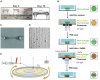
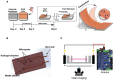

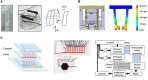

Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative organ-on-a-chip platforms for exploring tumorigenesis and therapy in head and neck cancer.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 16;23(1):798. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06824-5. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40671128 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sousa-Victor P, García-Prat L, Muñoz-Cánoves P. Control of satellite cell function in muscle regeneration and its disruption in ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2022;23:204–26. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

