Sevoflurane Alleviates Cardiomyocyte Ferroptosis via Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 7/Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Modulation
- PMID: 40717825
- PMCID: PMC12296640
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S524019
Sevoflurane Alleviates Cardiomyocyte Ferroptosis via Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 7/Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Modulation
Abstract
Background and objective: Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury remains a significant challenge in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction, highlighting the urgent need for effective cardioprotective strategies. Sevoflurane (Sev), a widely used anesthetic, has demonstrated notable cardioprotective potential. This study investigated whether Sev mitigates ferroptosis in myocardial cells by inhibiting the USP7-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway.
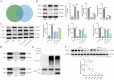
Methods: Rat myocardial I/R injury and H9c2 cell hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) injury models were established. Myocardial injury was assessed through cTnT levels, hemodynamic parameters, and histological analyses. Cell viability, LDH release, TUNEL staining, and ferroptosis markers (GSH, MDA, Fe²+, ROS) were evaluated. Co-IP and CHX assays were employed to explore USP7's regulation of PTEN stability.
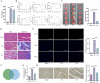
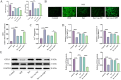
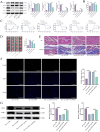
Results: Sev significantly reduced serum cTnT levels, improved hemodynamic function, decreased infarct size, and alleviated myocardial fibrosis and inflammation in rats subjected to I/R injury. In H9c2 cells, Sev enhanced cell viability and suppressed apoptosis. Sev reversed hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced USP7 overexpression and ferroptosis, whereas USP7 overexpression attenuated Sev's protective effects.
Conclusion: Sev protected against myocardial I/R injury by inhibiting USP7, destabilizing PTEN, activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, and suppressing ferroptosis. These findings elucidated the molecular mechanism of Sev's cardioprotective effect and suggested USP7 as a potential therapeutic target for myocardial protection.
Keywords: PTEN; USP7; ferroptosis; ischemia; sevoflurane.
© 2025 Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Puerarin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Damage by Targeting Ferroptosis through 14-3-3η Modulation.Am J Chin Med. 2025;53(5):1501-1520. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X25500570. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Am J Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40646505
-
Xanthosine alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through attenuation of cardiomyocyte ferroptosis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 28;30(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00766-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40722060 Free PMC article.
-
Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.J Mol Histol. 2025 Jun 27;56(4):207. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10453-z. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40576913
-
Inhibition of ubiquitin-specific protease 7 ameliorates ferroptosis-mediated myocardial infarction by contrasting oxidative stress: An in vitro and in vivo analysis.Cell Signal. 2024 Dec;124:111423. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111423. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 39304097
-
Protective effect of sevoflurane on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2024 Nov 1;110(11):7311-7330. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001975. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 39093878 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

