Evaluation of clopidogrel responsiveness using the Platelet Function Analyzer-200 (PFA-200) in dogs
- PMID: 40717918
- PMCID: PMC12292019
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1595147
Evaluation of clopidogrel responsiveness using the Platelet Function Analyzer-200 (PFA-200) in dogs
Abstract
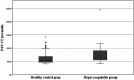
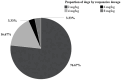
We aimed to evaluate the prevalence of clopidogrel resistance in hypercoagulable dogs using the Platelet Function Analyzer-200 (PFA-200) P2Y cartridge; further, we aimed to assess the utility of hematocrit (HCT), platelet count (PLT), prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), thromboelastography (TEG) parameters, and D-dimer level as indicators of clopidogrel efficacy. Forty healthy dogs underwent single measurements of P2Y closure time (CT), HCT, PLT, PT, aPTT, TEG parameters, and D-dimer levels, while thirty hypercoagulable dogs underwent two measurements of these parameters before and after clopidogrel treatment. The reference interval for P2Y CT in healthy dogs was 40.0-141.5 s, with a mean of 63.9 ± 26.82 s. Hypercoagulable dogs showed a mean baseline P2Y CT of 77.4 ± 37.6 s. Moreover, 23 (76.67%) and 7 (23.33%) showed responsiveness and resistance to the initial clopidogrel dose, respectively. The mean P2Y CT of the clopidogrel-resistant group after clopidogrel administration was 182.71 ± 78.43 s. Increasing the maintenance dose successfully overcame clopidogrel resistance in these seven dogs. Among the assessed parameters, only D-dimer levels showed a significant decrease in the clopidogrel-responder group (p < 0.05), suggesting its potential utility in evaluating responsiveness. In conclusion, the PFA-200 P2Y cartridge effectively detects clopidogrel resistance in dogs and can guide therapeutic adjustments such as dose escalation.
Keywords: P2Y cartridge; PFA; Platelet Function Analyzer; clopidogrel resistance; dogs.
Copyright © 2025 Shin and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of clopidogrel impact on canine platelet function using flow cytometry and thromboelastography platelet mapping.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jun 5;12:1555641. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1555641. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40538731 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Reference Intervals for the TEG 6s, a Point-of-Care Viscoelastic Assay, in Dogs.Vet Clin Pathol. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.1111/vcp.70027. Online ahead of print. Vet Clin Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40654288
-
Platelet count, spleen length, and platelet count-to-spleen length ratio for the diagnosis of oesophageal varices in people with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 26;4(4):CD008759. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008759.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28444987 Free PMC article.
-
Does Augmenting Irradiated Autografts With Free Vascularized Fibula Graft in Patients With Bone Loss From a Malignant Tumor Achieve Union, Function, and Complication Rate Comparably to Patients Without Bone Loss and Augmentation When Reconstructing Intercalary Resections in the Lower Extremity?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003599. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40569278
-
Clopidogrel used in combination with aspirin compared with aspirin alone in the treatment of non-ST-segment-elevation acute coronary syndromes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2004 Oct;8(40):iii-iv, xv-xvi, 1-141. doi: 10.3310/hta8400. Health Technol Assess. 2004. PMID: 15461878
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

