Is 2 h of Hypothermic Machine Perfusion for Pancreas Preservation Effective in Improving Graft Reperfusion?
- PMID: 40718054
- PMCID: PMC12289133
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001834
Is 2 h of Hypothermic Machine Perfusion for Pancreas Preservation Effective in Improving Graft Reperfusion?
Abstract
Background: Static cold storage (SCS) remains the standard method for organ preservation. The development of parenchymal edema during prolonged hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) was a major barrier to the introduction of this technique for the preservation of pancreases. A short period of HMP could optimize the pancreas for reperfusion while minimizing the side effects related to perfusion. Our objective is to evaluate the impact of short-term HMP on the pancreatic reperfusion.
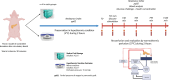
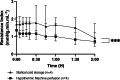
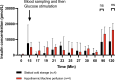
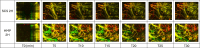
Methods: A preclinical study using a controlled donation after circulatory death porcine model was conducted. After procurement, the pancreases were preserved under hypothermic conditions for 2 h either by SCS (n = 4) or HMP (n = 4). After these 2 h of preservation, the pancreases were reperfused using a normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) for 2 h. During NMP, oxygenation, perfusion parameters, biochemical analyses, a glucose stimulation insulin secretion test, and an evaluation of ischemia/reperfusion injury by photoacoustic tomography were assessed.
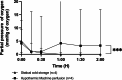
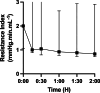
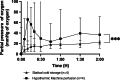
Results: During NMP, resistance indices were significantly lower in the HMP group compared with the SCS group, even after 2 h of reperfusion. The tissue oxygen partial pressure was higher throughout NMP after HMP preservation. Lactate and amylase levels were equal between the 2 groups. Lipase levels were higher in the HMP group. The glucose stimulation test showed no difference between the 2 groups. Photoacoustic tomography assessment showed no endothelial damage in either group.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that a short-term HMP applied to pancreases for 2 h is effective in reducing resistance indexes and improving oxygenation.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Transplantation Direct. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
B.M. and J.B. received grant funding and technical support from Institut Georges Lopez. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Normothermic and hypothermic machine perfusion preservation versus static cold storage for deceased donor kidney transplantation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 9;7(7):CD011671. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011671.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38979743 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreas Preservation: Hypothermic Oxygenated Perfusion to Improve Graft Reperfusion.Transplantation. 2025 Jan 1;109(1):e1-e10. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000005111. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Transplantation. 2025. PMID: 39656523
-
Machine perfusion in liver transplantation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Sep 12;9(9):CD014685. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014685.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37698189 Free PMC article.
-
Maximizing kidneys for transplantation using machine perfusion: from the past to the future: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Oct;95(40):e5083. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005083. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27749583 Free PMC article.
-
Does Normothermic Machine Perfusion Still Provide an Advantage for Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation? A Systematic Review and Preliminary Meta-Analysis.Artif Organs. 2025 May;49(5):749-761. doi: 10.1111/aor.14958. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Artif Organs. 2025. PMID: 39878386
References
-
- Ziaja J, Kolonko A, Kamińska D, et al. Long-term outcomes of kidney and simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation in recipients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: silesian experience. Transplant Proc. 2016;48:1681–1686. - PubMed
-
- Pérez Tamajón L, Marrero Miranda D, Caballero Figueroa A, et al. Improved cardiovascular risk profile of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and renal failure after simultaneous pancreas–kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:3979–3980. - PubMed
-
- Rajkumar T, Mazid S, Vucak-Dzumhur M, et al. Health-related quality of life following kidney and simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation. Nephrology (Carlton). 2019;24:975–982. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

