Resveratrol Alleviates Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion by Targeting Lingo-1, NgR1, p75, and RhoA/ROCK-2 Pathways
- PMID: 40718448
- PMCID: PMC12297015
- DOI: 10.5812/ijpr-158864
Resveratrol Alleviates Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion by Targeting Lingo-1, NgR1, p75, and RhoA/ROCK-2 Pathways
Abstract
Background: Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH), a pathophysiological state linked to vascular dementia and cognitive impairment, involves the NgR1/Lingo-1/p75 signaling complex implicated in neurodegenerative processes. Resveratrol (RES), a neuroprotective compound, was investigated for its potential to mitigate CCH-induced cognitive deficits by targeting this pathway.
Objectives: This study examined RES's ability to improve cognitive impairment in CCH by suppressing the NgR1/Lingo-1/p75 complex and downstream RhoA-ROCK2 signaling.
Methods: Rats were divided into five groups: Control, CCH + Ethanol (ETH), CCH, CCH + resveratrol (RES), and RES. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion was induced via permanent bilateral carotid artery occlusion (2VO). Cognitive function was assessed using the Morris Water Maze (MWM). Hippocampal morphology in CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus (DG) regions was analyzed via H&E staining. The expression levels of Lingo-1, NgR1, P75, RhoA, and ROCK2 signaling pathway were detected by western blot and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR).
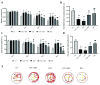
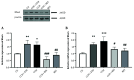
Results: Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats showed elevated protein expression of Lingo-1, p75, RhoA, and ROCK2, though NgR1 remained unchanged. The RES treatment significantly reduced these protein levels. Similarly, mRNA levels of all five targets increased in CCH, but RES notably lowered Lingo-1 and NgR1 expression. The MWM tests revealed RES improved spatial learning and memory deficits in 2VO rats. H&E staining demonstrated RES's neuroprotective effects, preserving hippocampal neuron integrity.
Conclusions: Resveratrol alleviates CCH-induced cognitive impairment by downregulating the Lingo-1/NgR1/p75 signaling axis and inhibiting RhoA-ROCK2 pathways. These findings highlight RES's potential as a therapeutic agent for vascular cognitive impairment associated with chronic hypoperfusion.
Keywords: Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion; Lingo-1; NgR1; Resveratrol; p75.
Copyright © 2025, Jamhiri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide Alleviates Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion: Associations with Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore Closure and Suppression of Excessive Mitophagy.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025 Jun 18;16(12):2208-2216. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00826. Epub 2025 May 29. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40440567 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-induced irisin ameliorates cognitive impairment following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by suppressing neuroinflammation and hippocampal neuronal apoptosis.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Jun 28;22(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03493-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40581647 Free PMC article.
-
[4'-O-methylbavachalcone improves vascular cognitive impairment by inhibiting neuroinflammation via EPO/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Jul;50(14):3990-4002. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250311.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40904086 Chinese.
-
Cytidinediphosphocholine (CDP-choline) for cognitive and behavioural disturbances associated with chronic cerebral disorders in the elderly.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD000269. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000269.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 15846601
-
The Bidirectional Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha in Vascular Dementia Caused by Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10398-10413. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04914-5. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40205304 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
