Beyond inflammation: the multifaceted therapeutic potential of targeting the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 40718478
- PMCID: PMC12289504
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1576371
Beyond inflammation: the multifaceted therapeutic potential of targeting the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
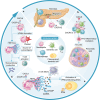
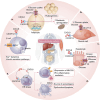
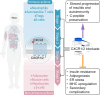
Identifying novel therapeutic targets involved in the multiple mechanisms underlying the complex pathophysiology of type 1 diabetes (T1D) could change the natural history of this disease. The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis is emerging as a therapeutic target with a crucial, multifaceted role in T1D pathophysiology. CXCL8-dependent neutrophil chemotaxis to the pancreas precedes autoimmunity, and CXCR1/2 blockade mitigates insulitis and T1D development in preclinical models. In parallel, CXCL8 can act in a β cell-autonomous manner, and exert non-immune actions on adipocytes, hepatocytes, podocytes, and muscle cells that contribute to insulin resistance and diabetic complications. In this review, we delineate compelling evidence of immune and non-immune actions of the axis in the onset and progression of T1D. We show that the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis represents a promising therapeutic target for the prevention/reversal of T1D, with a meaningful potential clinical advantage conveyed by its role in multiple components of the pathology and diabetic complications.
Keywords: CXCL8; CXCR1; CXCR2; chemokines; inflammation; interleukin-8; neutrophils; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 Fousteri, Jones, Novelli, Boccella, Brandolini, Aramini, Pozzilli and Allegretti.
Conflict of interest statement
RN, MJ, AA, LB, SB, and MA are employees of Dompé Farmaceutici S.p.A. GF was an employee of Dompé Farmaceutici S.p.A. at the time of writing. PP has received consulting fees from Dompé Farmaceutici S.p.A. The author(s) declared that MA is an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Interleukin-8/C-X-C Chemokine Receptor 2 Signaling Axis Prevents Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Pharmacology. 2025;110(3):178-190. doi: 10.1159/000545659. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Pharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40188812 Free PMC article.
-
The extra-islet pancreas supports autoimmunity in human type 1 diabetes.Elife. 2025 Apr 15;13:RP100535. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100535. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40232951 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR1/2 antagonism inhibits neutrophil function and not recruitment in cancer.Oncoimmunology. 2024 Jul 26;13(1):2384674. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2024.2384674. eCollection 2024. Oncoimmunology. 2024. PMID: 39076249 Free PMC article.
-
The CXCR1/2 Pathway: Involvement in Diabetes Pathophysiology and Potential Target for T1D Interventions.Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Oct;15(10):68. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0638-x. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 26275440 Review.
-
Targeting CXCR2 signaling in inflammatory lung diseases: neutrophil-driven inflammation and emerging therapies.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):9583-9607. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03970-x. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40047857 Review.
References
-
- Gregory GA, Robinson TIG, Linklater SE, Wang F, Colagiuri S, De Beaufort C, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2022) 10:741–60. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00218-2, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

