Assessing the Predictive Value of NLR and PLRs in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Receiving First-line Systemic Therapy: Observations from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan
- PMID: 40718611
- PMCID: PMC12288572
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1462
Assessing the Predictive Value of NLR and PLRs in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Receiving First-line Systemic Therapy: Observations from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan
Abstract
Background and aim: Inflammatory biomarkers are commonly utilized and remain a topic of ongoing discussion regarding their role in predicting outcomes in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The overall survival (OS) of patients with advanced HCC who received first-line systemic therapy at a tertiary care hospital in Pakistan was examined in this study in relation to the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) at baseline and 1 month after treatment.
Materials and methods: The study tracked 107 patients with advanced HCC from 2017 to 2024 who received atezolizumab/bevacizumab, lenvatinib, and sorafenib as therapy. Pretreatment and posttreatment (1 month) NLR and PLR values were analyzed. The most appropriate NLR and PLR cutoff thresholds were determined using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log-rank tests were used to determine OS.
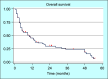
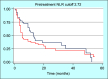
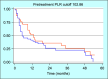
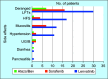
Results: Nine months was the median OS, with a 95% confidence interval (CI) ranging from 5 to 13.7 months. Patients with a pretreatment NLR below 2.72 had a median survival of 13 months (95% CI: 9-32 months), whereas those with an NLR of 2.72 or higher had a median survival of 5 months (95% CI: 4-11). Similarly, patients with a pretreatment PLR under 102.86 achieved a median survival of 13 months (95% CI: 9-32), while those with a PLR equal to or above 102.86 experienced a median survival of 5 months (95% CI: 4-14). Treatment-related side effects, including deranged liver function tests, led to dose adjustments in 83.9% of patients and significantly influenced survival outcomes.
Conclusions: Higher pretreatment NLR and PLR were related with lower survival outcomes in advanced HCC patients undergoing first-line systemic treatment. Although not statistically significant, these biomarkers show potential as predictive tools when integrated with established systems like Albumin-Bilirubin grading and Child-Pugh classification. Additional studies are required to validate their significance, particularly in the context of emerging therapies.
Clinical significance: The NLR and PLR, combined with established tools, offer a cost-effective approach to refine patient selection and improve outcomes in advanced HCC, particularly in resource-limited settings.
How to cite this article: Naviwala MSS, Tariq M, Saleem W, et al. Assessing the Predictive Value of NLR and PLRs in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Receiving First-line Systemic Therapy: Observations from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan. Euroasian J Hepato-Gastroenterol 2025;15(1):107-112.
Keywords: First-line treatment; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; Predictive assessment.
Copyright © 2025; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: NoneConflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Predictors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Various Treatments: a Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(3):967-981. doi: 10.1159/000485396. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29179180
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) as a Predictive Biomarker in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with First-Line Immunotherapy.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2025 Aug 19;56(1):175. doi: 10.1007/s12029-025-01299-5. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40830281
-
Analysis of factors influencing tumor volume doubling time in hepatocellular carcinoma and its predictive value for progression-free survival.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06349-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670432 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
