CPT1A mediated preservation of mitochondrial inhibits pyroptosis in pancreatic acinar cells
- PMID: 40718711
- PMCID: PMC12289652
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1577669
CPT1A mediated preservation of mitochondrial inhibits pyroptosis in pancreatic acinar cells
Abstract
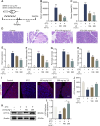
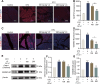
Introduction: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A (CPT1A) is crucial for mitochondrial function, and its dysfunction has been linked to the development of several diseases. However, the role of CPT1A in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) and its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Mitochondrial damage-mediated pyroptosis has been identified as a critical factor in pancreatic acinar cell death during SAP. this study aimed to evaluate the protective role of CPT1A in SAP and investigate its association with pancreatic acinar cell pyroptosis.
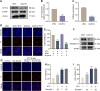
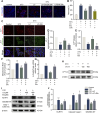
Methods: SAP models were established in male C57BL/6 mice by retrograde injection of 3% sodium taurocholate (STC) into the pancreatic duct and in primary acinar cells treated with 5 mM STC. Changes in Cpt1a mRNA and protein expression were assessed. Pancreatic pyroptosis was evaluated via activation of NLRP3 inflammasome-related proteins. Cpt1a was knocked down (siRNA) or inhibited (etomoxir) in cells. Cell viability was measured using Hoechst/PI staining, western blotting, and LDH release assays. The effects of CPT1A activators (C75, L-carnitine(LC)) on mitochondrial function (ΔΨm, mtROS, ox-mtDNA release) were examined in acinar cells.
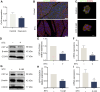
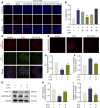
Results: In STC-induced SAP models (in vivo and in vitro), CPT1A expression was downregulated. Activating CPT1A with C75 or LC protected mitochondrial function (preserving ΔΨm, reducing mtROS, inhibiting ox-mtDNA release), thereby suppressing pyroptosis. LC treatment alleviated SAP in mice by inhibiting the NLRP3/GSDMD/Caspase-1 pathway and reducing acinar cell pyroptosis.
Discussion: These findings reveal a novel protective mechanism of CPT1A in SAP. Enhancing CPT1A activity preserves mitochondrial functions and suppresses NLRP3/GSDMD-mediated pancreatic acinar cell pyroptosis, highlighting CPT1A as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: CPT1A; L-carnitine; acute pancreatitis; mitochondrial dysfunction; pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Liu, Yu, Tian, Li, Gao, Bao, Wu, Zhang and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fenbufen Alleviates Severe Acute Pancreatitis by Suppressing Caspase-1/Caspase-11-mediated Pyroptosis in Mice.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024;17:e110523216783. doi: 10.2174/1874467217666230511095540. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37165681
-
Pancreatic stone protein inhibits pyroptosis of pancreatic acinar cells in sepsis-associated pancreatic injury.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 10;12:1566728. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1566728. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40708650 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial autophagy inhibits nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3-mediated pyroptosis and alleviates endothelial cell injury in pregnancy-induced hypertension.Cytojournal. 2025 Jun 12;22:60. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_52_2025. eCollection 2025. Cytojournal. 2025. PMID: 40708834 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeic acid ameliorates intestinal barrier injury to attenuate acute pancreatitis via inhibiting GSDMD-mediated pyroptotic pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 9;353(Pt A):120261. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120261. Online ahead of print. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40645541
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Different Adipose Tissue Depots Ameliorate Severe Acute Pancreatitis by Inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3/Caspase-1 Pathways.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025 Jun 23. doi: 10.1007/s12015-025-10922-8. Online ahead of print. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025. PMID: 40549290
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

