Analysis of cancer-associated glycosyltransferases reveals novel targets of non-small cell lung cancer pathogenesis
- PMID: 40718829
- PMCID: PMC12290921
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1601368
Analysis of cancer-associated glycosyltransferases reveals novel targets of non-small cell lung cancer pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: Aberrant glycosylation is associated with cancer progression and patient survival, of which the driving genes could act as biomarkers. Our objective was to characterize the expression of glycosylation-related genes to elucidate the heterogeneity between lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), and their prospective diagnostic utility.
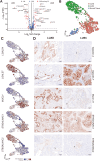
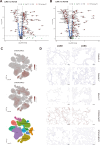
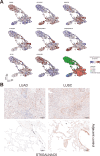
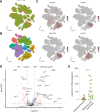
Methods: mRNA expression data for all glyco-relevant genes was collected from 553 LUSC and 576 LUAD patients from the TCGA dataset. Differential gene expression analysis and UMAP dimension reduction analysis were used to compare mRNA expression in LUAD and LUSC. Selected genes were further confirmed through immunohistochemistry of tissue biopsies. Public single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data from 72 LUSC and 163 LUAD patients was retrieved to study cell type-specific expression. Galectin-7 was measured in patients' plasma by ELISA. Univariate Cox proportional regression model was used for prognostic marker detection.
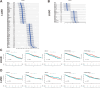
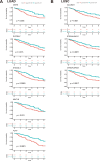
Results: Our analysis revealed genes differentially expressed respectively in LUSC and LUAD compared to normal lung samples. We focused on genes exhibiting high expression in LUSC (LGALS7, LGALS7B, and ST6GALNAC2) and in LUAD (LGALS4, MUC21, and ST6GALNAC1). Key glyco-related signatures were mostly observed in the malignant cell compartment. Galectin-7 concentration in plasma was upregulated in LUSC patients, but not LUAD patients. 67 genes in LUAD and 23 genes in LUSC were strongly linked to patient survival.
Conclusion: We identified several glyco-associated biomarkers in NSCLC, including Galectin-4, Galectin-7, MUC21, ST6GALNAC1, and ST6GALNAC2. Galectin-7 is a promising clinical biomarker for detection in plasma.
Keywords: galectins; glycosylation; mucins; non-small cell lung cancer; α2,6-GalNAc-sialylation.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, van Ee, Janssen, Rodríguez, Kim, Radonic, van Beusechem, Fransen, Bahce and van Kooyk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

