Circulating extracellular vesicles in facilitated stroke recovery via MiR-451-5p/MIF and MiR-451-5p/CCND1 axes
- PMID: 40719611
- PMCID: PMC12303924
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X251361247
Circulating extracellular vesicles in facilitated stroke recovery via MiR-451-5p/MIF and MiR-451-5p/CCND1 axes
Abstract
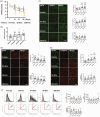
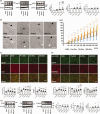
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from cells such as mesenchymal stem cells exert neurorestorative effects; however, the efficacy of circulating EVs for repairing injured brains and functional recovery after stroke remains unknown. This study shows that miR-451-5p in circulating EVs is crucial for stroke recovery, with its first therapeutic application in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) rats. Circulating EVs derived from MCAO rats in the chronic recovery phase were enriched in miR-451-5p, especially in CD9+ EVs., increased S100A10+ astrocytes and decreased C3d+ astrocytes in the peri-infarct area (PIA). They also increased axonemal phosphorylated high-molecular-weight neurofilaments and dendritic non-phosphorylated high-molecular-weight neurofilaments, reduced the infarct size, and enhanced functional recovery. EVs with miR-451-5p overexpression suppressed macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cultured neurons and cyclin D1 in cultured astrocytes after stroke. These findings indicate that miR-451-5p-enriched CD9+ circulating EVs restored ischemic brain tissues, making them potential therapeutic targets for stroke.
Keywords: Circulating EVs; cyclin D1; ischemic stroke; macrophage migration inhibitory factor; miR-451-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Pekny M, Wilhelmsson U, Tatlisumak T, et al. Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis-a new target in stroke? Neurosci Lett 2019; 689: 45–55. - PubMed
-
- Hira K, Ueno Y, Tanaka R, et al. Astrocyte-derived exosomes treated with a semaphorin 3a inhibitor enhance stroke recovery via prostaglandin D2 synthase. Stroke 2018; 49: 2483–2494. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

