Closing Gaps in Chronic Kidney Disease Detection: Evaluating At-Home Targeted Testing in a Safety-Net Population
- PMID: 40719700
- PMCID: PMC12304639
- DOI: 10.1177/21501319251358923
Closing Gaps in Chronic Kidney Disease Detection: Evaluating At-Home Targeted Testing in a Safety-Net Population
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States, yet 90% of those impacted remain unaware of their condition, and fewer than 20% of at-risk individuals are appropriately tested. Safety-net health care settings are disproportionately burdened by CKD, with a patient population enriched for CKD risk factors, social deprivation, and barriers to diagnostic testing which delay access to diagnosis and lifesaving interventions. The National Kidney Foundation partnered with a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) to evaluate an approach to increase guideline-recommended testing among patients at high-risk for developing CKD.
Methods: Through electronic health record (EHR) data analysis, eligible patients were identified to receive an at-home, semi-quantitative urine albumin-creatine ratio (uACR) testing kit. The kits provided immediate results via a smartphone application, as well as automatically routed to the clinic EHR for the patient's provider to coordinate necessary follow-up care. This initiative was conducted in Missouri, USA in 2023 and evaluated using domains of the Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance (RE-AIM) framework.
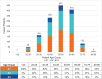
Results: Results reflect that 1496 of 4677 (32%) eligible patients completed uACR testing with 50% receiving abnormal results indicative of albuminuria. Of those with evidence of albuminuria, 84% had follow-up visits and 32% completed appropriate follow-up testing based on clinical guidelines. Albuminuria was prevalent across all age groups, with 69% of abnormal results appearing in patients under 60 years. Consistent with national data, patients identifying as Black were significantly more likely to have albuminuria in this cohort (P < .0001). Notably, most patients with albuminuria had an eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Conclusions: Findings highlight the urgency of improving uACR testing for early CKD diagnosis, especially in safety-net settings. The findings also demonstrate the utility of at-home testing to improve access to care across underserved communities and represent a replicable, efficient model to identify those with high risk of CKD progression. While the program required significant time and coordination, this can be streamlined for analogous programs. Future opportunities exist to further the impacts including additional quality improvement activities to ensure follow-up testing and close gaps in CKD care.
Keywords: at-home testing; chronic kidney disease; diabetes; disparities; federally qualified health center; population health.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Joseph A. Vassalotti, MD: (1) Novo Nordisk, Inc.—consultant US Nephrology Advisory Board in June 2024 on the FLOW trial for semaglutide (Ozempic) impact on nephrology—no speaking role. (2) Sanofi, Inc. OTC Consultant on the oseltamivir (Tamiflu) approach to over-the-counter use of antiviral medication that requires dose adjustment for CKD with low eGFR—no speaking role. Leslie Lake is now with a new institution since completing the project (see Author Note Section).
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2025. Accessed February 1, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/kidney-disease/php/data-research/index.html
-
- Kidney Disease Surveillance System. Trends in Prevalence of CKD among U.S. Adults with Hypertension. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2025. Accessed February 1, 2025. https://nccd.cdc.gov/CKD/detail.aspx?Qnum=Q764#refreshPosition
-
- Kidney Disease Surveillance System. Trends in Prevalence of CKD among U.S. Adults with Diabetes. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2025. Accessed February 1, 2025. https://nccd.cdc.gov/CKD/detail.aspx?Qnum=Q763&topic=4#refreshPosition
-
- van der Velde M, Matsushita K, Coresh J, et al. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. A collaborative meta-analysis of high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011;79(12):1341-1352. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.536 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

