TIGAR inhibits glucose-metabolism and cisplatin-chemosensitivity in human lung cancer cells
- PMID: 40719984
- PMCID: PMC12304353
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03274-9
TIGAR inhibits glucose-metabolism and cisplatin-chemosensitivity in human lung cancer cells
Abstract
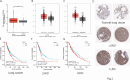
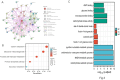
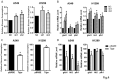
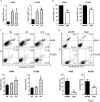
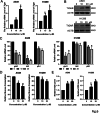
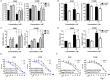
TIGAR is an important factor associated with tumor glucose metabolism, but its function and underlying mechanism in human lung cancer remains unclear. Here, we analyzed the expression changes, prognosis, genetic alteration, related gene networks and metabolic pathways of TIGAR in lung cancer. The findings revealed that TIAGR level was augmented in LUAD and LUSC in comparison to the normal lung tissue. In addition, high TIAGR level was related to poorer outcome of patients with LUAD. Different alterations in TIGAR gene at various sites were observed in both LUAD and LUSC. The GO/KEGG analyses indicated that TIGAR affects the occurrence and progress of lung cancer through multiple metabolic pathways. Further, we established lung cancer cell models with TIGAR knockdown or overexpression to explore its effects on glucose metabolism, apoptosis and chemosensitivity. Our results indicated that TIGAR markedly inhibited glucose metabolism, ROS production, and susceptibility of lung cancer cells to cisplatin. Together, TIGAR plays a cancer-promoting role in lung cancer, which becomes a promising prognostic and therapeutic biomarker.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Chemosensitivity; Lung cancer; Metabolism; TIGAR.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12(1):31–46. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
