Germicidal UV Light and Incidence of Acute Respiratory Infection in Long-Term Care for Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 40720106
- PMCID: PMC12305439
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2025.3388
Germicidal UV Light and Incidence of Acute Respiratory Infection in Long-Term Care for Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Infectious outbreaks of respiratory viruses within long-term care facilities (LTCFs) for older adults are associated with high rates of hospitalization and death. Despite evidence that airborne transmission contributes substantially to the spread of respiratory viruses within residential care for older adults, this mode of transmission has been largely unaddressed by existing infection control practices.
Objective: To determine whether germicidal UV (GUV) appliances reduce acute respiratory infection (ARI) incidence in LTCFs.
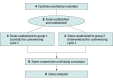
Design, setting, and participants: This multicenter, 2-arm, double-crossover, cluster randomized clinical trial assessed the effectiveness of GUV appliances in common spaces on the incidence of ARIs in 4 LTCFs in metropolitan and regional South Australia. LTCFs were divided into 2 equally sized zones (mean [SD] size, 44 [9] beds per zone). Within each LTCF, zones were randomized to active GUV appliances (intervention) or inactive (control) for 6 weeks, which was followed by a 2-week washout, crossover, and a further 2-week washout. Seven consecutive cycles were performed during the 110-week study period from August 31, 2021, to November 13, 2023. Data were analyzed from January 18, 2024, to December 4, 2024.
Intervention: Continuous GUV appliance activity within common (non-resident room) areas for 6 weeks.
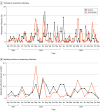
Main outcome and measures: The primary outcome was the incidence rate of ARIs (per zone per cycle). A secondary analysis of long-term trends was performed based on infections per week.
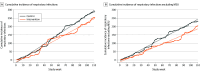
Results: Eight assessed zones across 4 LTCFs represented a total of 211 952 bed-days. Of 596 ARIs recorded across all zones, 475 (79.7%) occurred during intervention or control periods. The incidence rate in the control arm was 4.17 infections per zone per cycle (95% CI, 2.43-5.91), compared with 3.81 infections per zone per cycle (95% CI, 2.21-5.41) in the intervention arm (incidence rate ratio, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.77-1.09; P = .33). A posteriori secondary analysis with time-series autoregressive modeling showed that the control group recorded 2.61 ARIs per week (95% CI, 2.51-2.70) compared with 2.29 ARIs per week (95% CI, 2.06-2.51) in the intervention group (mean difference, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.10-0.54; P = .004).
Conclusions and relevance: This randomized clinical trial found that GUV light appliances in common areas of LTCFs did not reduce the incidence rate of ARIs per zone per cycle but did modestly reduce the total numbers of ARIs by the study conclusion. GUV appliances might be considered to support existing infection prevention and control practices in these settings.
Trial registration: Australian and New Zealand Clinical Trial Registration: ACTRN12621000567820.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
Can Upper-Room UV Light Prevent Nosocomial Respiratory Viral Infections?JAMA Intern Med. 2025 Sep 1;185(9):1136-1137. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2025.3403. JAMA Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40720147 No abstract available.
References
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics . Deaths due to acute respiratory infections in Australia—2022-March 2024. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.abs.gov.au/articles/deaths-due-acute-respiratory-infections-...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

