In vitro and in vivo characterization of wild type BMP9 and a non-osteogenic variant in models of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 40720495
- PMCID: PMC12303310
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329089
In vitro and in vivo characterization of wild type BMP9 and a non-osteogenic variant in models of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
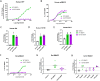
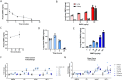
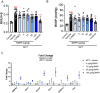
Endothelial dysfunction and the resulting vascular remodeling are hallmarks of pulmonary hypertension, a debilitating disease of high arterial pressure in the lungs and the right side of the heart. Mutations in the BMPR2 signaling pathway are associated with the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Previous pre-clinical studies demonstrated that exogenous administration of recombinant human wild type BMP9 (WT BMP9) enhances BMPR2/ALK1 mediated signaling and reverses experimental pulmonary hypertension in rat models. However, BMP9 induces osteogenic activity in progenitor cells through activation of ActR2A and ActR2B receptor complexes potentially leading to unwanted bone formation in non-osteogenic tissues. The cellular activity of human WT BMP9 and amino acid substitution variants was characterized in vitro in terms of BMPR2 and ActR2 signaling. We identified a mutant variant of human BMP9 that maintains its activity in endothelial cells, specifically preserving BMPR2 signaling while eliminating osteogenic signaling associated with ActR2A/B activation in mesenchymal precursor cells. Rat models of pulmonary hypertension served as in vivo models to characterize efficacy and safety of BMP9 supplementation therapy. While WT BMP9 effectively activates BMPR2 signaling across species in rat, cynomolgus monkey and human systems, our human BMP9 mutant variant is inactive on rat BMPR2/ALK1 receptor complexes. Therefore, WT BMP9 was used to examine disease reversal in the preclinical monocrotaline model rat of pulmonary hypertension. WT BMP9 failed to improve right ventricular systolic pressure or right ventricular hypertrophy, despite clear target engagement shown by upregulation of SMAD7. Telemetry studies of WT BMP9 in the Sugen 5416 and hypoxia rat model of pulmonary hypertension indicated no significant change in pulmonary pressure but led to increased systemic blood pressure and decreased heart rate. Additionally, escalating doses in naive rats caused severe dose-limiting effects and morbidity at 500 µg/kg/day or higher. Given these findings including the absence of therapeutic efficacy in a relevant PAH animal model and dose limiting toxicity in rats, a therapeutic window for BMP9 treatment could not be established.
Copyright: © 2025 Schips et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are or were employees of Johnson and Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development: Janssen Research and Development LLC. This study was funded by Johnson and Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development: Janssen Research and Development LLC. The funder provided support in the form of salaries for authors, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ section. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

