Extracellular Vesicles for Clinical Diagnostics: From Bulk Measurements to Single-Vesicle Analysis
- PMID: 40720603
- PMCID: PMC12356129
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5c00706
Extracellular Vesicles for Clinical Diagnostics: From Bulk Measurements to Single-Vesicle Analysis
Abstract
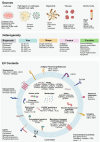
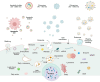
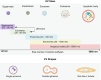
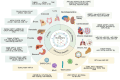
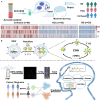
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a crucial role in intercellular communication, signaling pathways, and disease pathogenesis by transporting biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids derived from their cells of origin, and they have demonstrated substantial potential in clinical applications. Their clinical significance underscores the need for sensitive methods to fully harness their diagnostic potential. In this comprehensive review, we explore EV heterogeneity related to biogenesis, structure, content, origin, sample type, and function roles; the use of EVs as disease biomarkers; and the evolving landscape of EV measurement for clinical diagnostics, highlighting the progression from bulk measurement to single vesicle analysis. This review covers emerging technologies such as single-particle tracking microscopy, single-vesicle RNA sequencing, and various nanopore-, nanoplasmonic-, immuno-digital droplet-, microfluidic-, and nanomaterial-based techniques. Unlike traditional bulk analysis methods, these methods contribute uniquely to EV characterization. Techniques like droplet-based single EV-counting enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), proximity-dependent barcoding assays, and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy further enhance our ability to precisely identify biomarkers, detect diseases earlier, and significantly improve clinical outcomes. These innovations provide access to intricate molecular details that expand our understanding of EV composition, with profound diagnostic implications. This review also examines key research challenges in the field, including the complexities of sample analysis, technique sensitivity and specificity, the level of detail provided by analytical methods, and practical applications, and we identify directions for future research. This review underscores the value of advanced EV analysis methods, which contribute to deep insights into EV-mediated pathological diversity and enhanced clinical diagnostics.
Keywords: analytical techniques; biomarkers; diagnostics; extracellular vesicles (EVs); single EV analysis.
Figures













References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

