Enhancing Surgical Safety and Efficiency: Systematic Review and Single-Arm Meta-Analysis of Surgical Data Recorders
- PMID: 40720888
- PMCID: PMC12303543
- DOI: 10.2196/72703
Enhancing Surgical Safety and Efficiency: Systematic Review and Single-Arm Meta-Analysis of Surgical Data Recorders
Abstract
Background: Recently, surgical data recorders that are comparable to flight data recorders, also known as black boxes in the aviation industry, have been developed to improve patient safety and performance in surgery. These devices allow for unique insights in the operating room by providing new data capture capabilities. No systematic review has been carried out to evaluate the areas of application of surgical data recorders to date.
Objective: This systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis aims to assess the aspects of the operating theater environment for which surgical data recorders are used and to make a preliminary assessment of the quantifiable data that can be collected, compared to traditional collection methods.
Methods: This systematic review followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. Medline, Embase, and Web of Science databases were lastly systematically searched for papers that focused on a clinical use case for surgical data recorders on February 10, 2025. In particular, not relevant papers focusing on implementation of surgical data recorders were excluded. Title, abstract, and full-text screening were completed to identify relevant articles. The included studies were analyzed descriptively using data extraction forms. Where possible, quantifiable data was also analyzed. Risk of bias was assessed using the Risk Of Bias In Non-Randomized Studies of Exposure (ROBINS-E) tool.
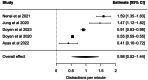
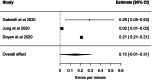
Results: In total, 70 studies were screened, and a total of 17 studies were included. A total of 10 of the 17 studies had a low overall risk of bias; however, confounding, selection bias, small sample sizes, short study periods, and potential Hawthorne effects were the notable limitations. Only 2 studies were assessed to have publication bias. Use cases could be grouped into 4 categories: economic, safety, behavior in the operating room, and technical skill assessment. A single-arm meta-analysis focusing on adverse events and distractions in the operating theater could be conducted, demonstrating accurate reporting of distractions in line with the existing literature.
Conclusions: Surgical data recorders provide an unobstructed view of various aspects of the operating theatre. Most published papers present preliminary studies on surgical data recorders, indicating the potential for further, larger-scale studies with enhanced methodological quality.
Keywords: healthcare technology; intraoperative monitoring; medical error reduction; meta-analysis; operating room; outcome assessment; patient safety; safety behavior; surgical data recorders; surgical performance.
© Niels Siegel, André Rotärmel, Georgios Polychronidis, Gabriel Salg, Rosa Klotz, Pascal Probst, Thomas Pausch. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
References
-
- Vidović A, Franjić A, Štimac I, Ban MO. The importance of flight recorders in the aircraft accident investigation. Transportation Research Procedia. 2022;64:183–190. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2022.09.022. doi. - DOI
-
- Kontogiannis T, Malakis S. A proactive approach to human error detection and identification in aviation and air traffic control. Saf Sci. 2009 May;47(5):693–706. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2008.09.007. doi. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

