Comparative Performance of Chatbots in Endodontic Clinical Decision Support: A 4-Day Accuracy and Consistency Study
- PMID: 40720933
- PMCID: PMC12319550
- DOI: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.100920
Comparative Performance of Chatbots in Endodontic Clinical Decision Support: A 4-Day Accuracy and Consistency Study
Abstract
Introduction and aims: Despite the use of artificial intelligence, which is increasingly prevalent in healthcare settings, concerns remain regarding its reliability and accuracy. The study assessed the overall, difficulty level-specific, and day-to-day accuracy and consistency of 5 AI chatbots-ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4.o, Gemini 2.0 Flash, Copilot, and Copilot Pro-in answering clinically relevant endodontic questions.
Methods: Seventy-six correct/incorrect questions were developed by 2 endodontists and categorized by an expert into 3 difficulty levels (Basic [B]-, Intermediate [I]-, and Advanced [A]- level]. Twenty questions from each difficulty level were selected from a set of 74 validated questions (B, n = 26; I, n = 24; A, n = 24), resulting in a total of 60 questions. The questions were asked of the chatbots over a period of 4 days, at 3 different times each day (morning, afternoon, and evening).
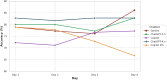
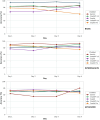
Results: ChatGPT-4.o achieved the highest overall accuracy (82.5%) and perfect performance in the B-level category (95.0%), while Copilot Pro had the lowest accuracy (74.03%). Gemini and ChatGPT-3.5 showed similar overall accuracy. Gemini's accuracy significantly improved over time, whereas significant decreases were noted in the Copilot Pro model across days, and no significant change was detected in both ChatGPT models and Copilot. In the B-level category, while Copilot Pro showed a significant decrease in accuracy rates, and in the B- and I-level categories, Copilot showed a significant increase in accuracy rates over the days. In the A-level category, Gemini demonstrated a significant increase in accuracy rates over the days.
Conclusions: ChatGPT-4.o demonstrated superior performance, whereas Copilot and Copilot Pro showed insufficient accuracy. ChatGPT-3.5 and Gemini may be acceptable for general queries but require caution in more advanced cases.
Clinical relevance: ChatGPT-4.o demonstrated the highest overall accuracy and consistency in all question categories over 4 days, suggesting its potential as a reliable tool for clinical decision-making.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; ChatGPT; Clinical decision support; Copilot; Endodontics; Gemini.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy and Reliability of Artificial Intelligence Chatbots as Public Information Sources in Implant Dentistry.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025 Jun 25;0(0):1-23. doi: 10.11607/jomi.11280. Online ahead of print. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025. PMID: 40560758
-
Accuracy of ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4o, Copilot, Gemini, Claude, and Perplexity in advising on lumbosacral radicular pain against clinical practice guidelines: cross-sectional study.Front Digit Health. 2025 Jun 27;7:1574287. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1574287. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40657647 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative performance of ChatGPT, Gemini, and final-year emergency medicine clerkship students in answering multiple-choice questions: implications for the use of AI in medical education.Int J Emerg Med. 2025 Aug 7;18(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12245-025-00949-6. Int J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40775272 Free PMC article.
-
Current Applications of Chatbots Powered by Large Language Models in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: A Systematic Review.Dent J (Basel). 2025 Jun 11;13(6):261. doi: 10.3390/dj13060261. Dent J (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40559164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eggmann F., Blatz MB. ChatGPT: chances and challenges for dentistry. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2023;44:220–224. - PubMed
-
- Fergus S., Botha M., Ostovar M. Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. J Chem Educ. 2023;100:1672–1675. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00087. - DOI
-
- Nazi Z., Peng W. Large language models in healthcare and medical domain: a review. Informatics. 2024;11:57. doi: 10.3390/informatics11030057. - DOI
-
- Arslan B., Eyupoglu G., Korkut S., et al. The accuracy of AI-assisted chatbots on the annual assessment test for emergency medicine residents. J Med Surg Public Health. 2024;3 doi: 10.1016/j.glmedi.2024.100070. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources